Concurrent Pansinusitis and Orbital Cellulitis Complicated by Extensive Head and Neck Venous Thrombosis in an Unvaccinated Adolescent Patient with COVID-19: A Case Report
- PMID: 37336653
- PMCID: PMC10022179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2023.03.062
Concurrent Pansinusitis and Orbital Cellulitis Complicated by Extensive Head and Neck Venous Thrombosis in an Unvaccinated Adolescent Patient with COVID-19: A Case Report
Abstract
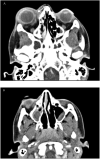
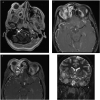
Background: Orbital cellulitis is an infrequent but serious infectious complication of rhinosinusitis, most commonly seen in the pediatric population. Extension into the cavernous sinus, leading to further infection and thrombosis, is a rare but life-threatening complication. Although COVID-19 has been linked to an increased risk of venous thromboembolism, most cases involve extremity deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism; reports of intracranial or jugular system thrombosis are rare.
Case report: We describe a case of a 17-year-old female patient with no significant medical history or thrombotic risk factors found to have orbital cellulitis and severe pansinusitis, complicated by multiple venous thromboses in the head and neck requiring emergent surgical intervention and pediatric intensive care admission. WHY SHOULD AN EMERGENCY PHYSICIAN BE AWARE OF THIS?: Extensive head and neck venous thrombosis and intracranial abscesses are rare complications of pansinusitis and orbital cellulitis, and the thrombotic complications of COVID-19 are well documented. A delay in diagnosis and treatment can lead to potentially devastating consequences.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cavernous sinus thrombosis; Internal jugular vein thrombosis; Intracranial abscess; Orbital cellulitis; Pansinusitis; Pediatric; SARS-CoV-2; Streptococcus constellatus, Ophthalmic vein thrombosis.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Botting AM, McIntosh D, Mahadevan M. Paediatric pre- and post-septal peri-orbital infections are different diseases. A retrospective review of 262 cases. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;72:377–383. - PubMed
-
- Nageswaran S, Woods CR, Benjamin DK, Jr, Givner LB, Shetty AK. Orbital cellulitis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:695–699. - PubMed
-
- Seltz LB, Smith J, Durairaj VD, Enzenauer R, Todd J. Microbiology and antibiotic management of orbital cellulitis. Pediatrics. 2011;127:e566–e572. - PubMed
-
- Sobol SE, Marchand J, Tewfik TL, Manoukian JJ, Schloss MD. Orbital complications of sinusitis in children. J Otolaryngol. 2002;31:131–136. - PubMed
-
- Erickson BP, Lee WW. Orbital cellulitis and subperiosteal abscess: a 5-year outcomes analysis. Orbit. 2015;34:115–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

