The correlations between C-reactive protein and MRI-detected inflammation in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37336841
- PMCID: PMC10412674
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-023-06658-w
The correlations between C-reactive protein and MRI-detected inflammation in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: C-reactive protein (CRP) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are widely used to monitor inflammation in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), but the relationship between CRP and MRI-detected inflammation is incompletely understood. The present study was undertaken to assess correlations between CRP and MRI-detected inflammation in axSpA.
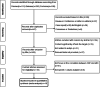
Materials and methods: A systematic literature search was performed (Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Library) to identify relevant studies concerning CRP and MRI-detected inflammation in axSpA patients. The MRI-detected inflammation was evaluated by MRI-based disease activity score (DAS). The correlation between CRP and MRI-based DAS was integrated by random-effect models.
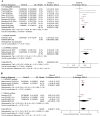
Results: Eighteen studies reported a total of 1392 axSpA patients which were included in this meta-analysis. CRP was significantly associated with spinal MR DAS (r=0.226, 95%CI [0.149, 0.291], p<0.001, I2=23%). We also found a moderate correlation between CRP change and spinal MR DAS change (r[ASspiMRI-a]=0.354, 95%CI [0.282, 0.422], p<0.001, I2=48%; r[SPARCC]=0.544, 95%CI [0.345, 0.701], p<0.001, I2=19%). CRP at baseline was negatively associated with improvement in spinal MR DAS (r= - 0.327, 95%CI [-0.397, -0.264], p<0.001, I2=0%). However, no significant association was found between CRP and sacroiliac joint (SIJ) MR DAS.
Conclusions: In axSpA patients, CRP is associated with MRI-detected inflammation in the spine but not in SIJ. We speculate that CRP could be a reasonable index to reflect spinal inflammation. Therefore, we suggest it is not essential to repeat spinal MRI in a short term, while SIJ MRI may be necessary to provide additional information on inflammation. Key Points • CRP is associated with MRI-detected inflammation in the spine but not in sacroiliac joints. • CRP at baseline was negatively associated with improvement in spinal MR DAS. • It was not essential to repeat spinal MRI frequently, while SIJ MRI may be necessary to provide additional information on inflammation.
Keywords: Axial spondyloarthritis; C-reactive protein; Disease activity; Magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

