Recovery of fuel from real waste oily sludge via a new eco-friendly surfactant material used in a digital baffle batch extraction unit
- PMID: 37336952
- PMCID: PMC10279633
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-37188-9
Recovery of fuel from real waste oily sludge via a new eco-friendly surfactant material used in a digital baffle batch extraction unit
Abstract
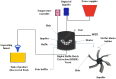
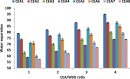
This study focused on developing a new cocktail extraction agent (CEA) composed of solvent and a new surfactant material (SM) for enhancing the efficiency of fuel recovery from real waste oil sludge (WSO). The effects of different solvents (e.g. methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), naphtha, petrol and kerosene), SMs (Dowfax and sodium thiosulfate), extraction time (10-20 min), extraction temperatures (20-60 °C) and CEA/sludge ratios (1-4) on the extraction performance were investigated. SMs and DBBE design enhanced the extraction efficiency by increasing the dispersion of solvent in WSO and enhancing the mixing and mass transfer rates. Results proved that Dowfax was the best SM for oil recovery under various conditions. The best CEA (e.g. MEK and Dowfax) provides the maximum fuel recovery rate of 97% at a period of 20 min, temperature of 60 °C and 4:1 CEA/sludge ratio. The produced fuel was analysed and fed to the distillation process to produce diesel oil. The characteristics of diesel oil were measured, and findings showed that it needs treatment processes prior its use as a finished fuel.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Che HNH, et al. Potential of Jatropha curcas L. as biodiesel feedstock in Malaysia: A concise review. Processes. 2020;8(7):786. doi: 10.3390/pr8070786. - DOI
-
- Humadi JI, et al. Fast, non-extractive, and ultradeep desulfurization of diesel in an oscillatory baffled reactor. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021;152:178–187. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.05.028. - DOI
-
- Al-Khodor, Y. A. A., & Albayati, T. M. Real heavy crude oil desulfurization onto nanoporous activated carbon implementing batch adsorption process: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Chemistry Africa 1–10 (2022).
-
- Kadhum, A. T. & Albayati, T. M. Desulfurization techniques process and future challenges for commercial of crude oil products. In AIP Conference Proceedings (AIP Publishing LLC, 2022).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

