Conserved allosteric inhibitory site on the respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerases
- PMID: 37337079
- PMCID: PMC10279679
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-04990-0
Conserved allosteric inhibitory site on the respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerases
Abstract
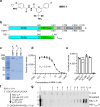
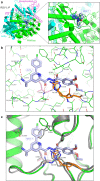
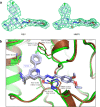
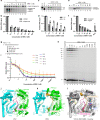
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human metapneumovirus (HMPV) are related RNA viruses responsible for severe respiratory infections and resulting disease in infants, elderly, and immunocompromised adults1-3. Therapeutic small molecule inhibitors that bind to the RSV polymerase and inhibit viral replication are being developed, but their binding sites and molecular mechanisms of action remain largely unknown4. Here we report a conserved allosteric inhibitory site identified on the L polymerase proteins of RSV and HMPV that can be targeted by a dual-specificity, non-nucleoside inhibitor, termed MRK-1. Cryo-EM structures of the inhibitor in complexes with truncated RSV and full-length HMPV polymerase proteins provide a structural understanding of how MRK-1 is active against both viruses. Functional analyses indicate that MRK-1 inhibits conformational changes necessary for the polymerase to engage in RNA synthesis initiation and to transition into an elongation mode. Competition studies reveal that the MRK-1 binding pocket is distinct from that of a capping inhibitor with an overlapping resistance profile, suggesting that the polymerase conformation bound by MRK-1 may be distinct from that involved in mRNA capping. These findings should facilitate optimization of dual RSV and HMPV replication inhibitors and provide insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying their polymerase activities.
© 2023. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates.
Conflict of interest statement
D.B., M.E., T.F., K.G., X.H., Y.H., J.H., D.K., B.L., D.M., E.M., T.M., and D.N. are current employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and potentially own stock and/or hold stock options in Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. Work in the RF lab was sponsored by Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. At the time of manuscript preparation, the RF lab also has sponsored research agreements with F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Ltd. and Enanta Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

