Genome-wide association analyses define pathogenic signaling pathways and prioritize drug targets for IgA nephropathy
- PMID: 37337107
- PMCID: PMC11824687
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01422-x
Genome-wide association analyses define pathogenic signaling pathways and prioritize drug targets for IgA nephropathy
Abstract
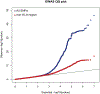
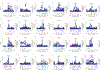
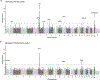
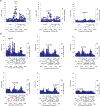
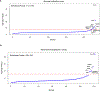
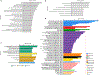
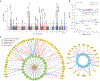
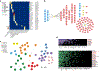
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is a progressive form of kidney disease defined by glomerular deposition of IgA. Here we performed a genome-wide association study of 10,146 kidney-biopsy-diagnosed IgAN cases and 28,751 controls across 17 international cohorts. We defined 30 genome-wide significant risk loci explaining 11% of disease risk. A total of 16 loci were new, including TNFSF4/TNFSF18, REL, CD28, PF4V1, LY86, LYN, ANXA3, TNFSF8/TNFSF15, REEP3, ZMIZ1, OVOL1/RELA, ETS1, IGH, IRF8, TNFRSF13B and FCAR. The risk loci were enriched in gene orthologs causing abnormal IgA levels when genetically manipulated in mice. We also observed a positive genetic correlation between IgAN and serum IgA levels. High polygenic score for IgAN was associated with earlier onset of kidney failure. In a comprehensive functional annotation analysis of candidate causal genes, we observed convergence of biological candidates on a common set of inflammatory signaling pathways and cytokine ligand-receptor pairs, prioritizing potential new drug targets.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures






Comment in
-
Building Toward Clinical Translation: New Study Refines Genetic Architecture of IgA Nephropathy.Am J Kidney Dis. 2024 Jan;83(1):108-111. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.09.001. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024. PMID: 37716417 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yu XQ et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies multiple susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet 44, 178–182 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI152960/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI130830/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR073228/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI149431/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI150748/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI150585/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DK116690/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM013061/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103311/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS099068/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK105124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010730/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI148276/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008680/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001834/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

