X-linked genes influence various complex traits in dairy cattle
- PMID: 37337145
- PMCID: PMC10278306
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09438-7
X-linked genes influence various complex traits in dairy cattle
Abstract
Background: The search for quantitative trait loci (QTL) affecting traits of interest in mammals is frequently limited to autosomes, with the X chromosome excluded because of its hemizygosity in males. This study aimed to assess the importance of the X chromosome in the genetic determinism of 11 complex traits related to milk production, milk composition, mastitis resistance, fertility, and stature in 236,496 cows from three major French dairy breeds (Holstein, Montbéliarde, and Normande) and three breeds of regional importance (Abondance, Tarentaise, and Vosgienne).
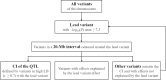
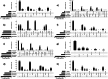
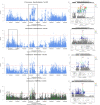
Results: Estimates of the proportions of heritability due to autosomes and X chromosome (h²X) were consistent among breeds. On average over the 11 traits, h²X=0.008 and the X chromosome explained ~ 3.5% of total genetic variance. GWAS was performed within-breed at the sequence level (~ 200,000 genetic variants) and then combined in a meta-analysis. QTL were identified for most breeds and traits analyzed, with the exception of Tarentaise and Vosgienne and two fertility traits. Overall, 3, 74, 59, and 71 QTL were identified in Abondance, Montbéliarde, Normande, and Holstein, respectively, and most were associated with the most-heritable traits (milk traits and stature). The meta-analyses, which assessed a total of 157 QTL for the different traits, highlighted new QTL and refined the positions of some QTL found in the within-breed analyses. Altogether, our analyses identified a number of functional candidate genes, with the most notable being GPC3, MBNL3, HS6ST2, and DMD for dairy traits; TMEM164, ACSL4, ENOX2, HTR2C, AMOT, and IRAK1 for udder health; MAMLD1 and COL4A6 for fertility; and NRK, ESX1, GPR50, GPC3, and GPC4 for stature.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the importance of the X chromosome in the genetic determinism of complex traits in dairy cattle and highlights new functional candidate genes and variants for these traits. These results could potentially be extended to other species as many X-linked genes are shared among mammals.
Keywords: Dairy cattle; GWAS; Meta-analyses; X chromosome.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

