Pay-it-forward gonorrhea and chlamydia testing among men who have sex with men and male STD patients in China: the PIONEER pragmatic, cluster randomized controlled trial protocol
- PMID: 37337181
- PMCID: PMC10280958
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-023-16095-8
Pay-it-forward gonorrhea and chlamydia testing among men who have sex with men and male STD patients in China: the PIONEER pragmatic, cluster randomized controlled trial protocol
Abstract
Background: Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) among men who have sex with men (MSM) in China. Previous studies have shown pay-it-forward (PIF) interventions to be associated with a substantial increase in gonorrhea and chlamydia test uptake compared to standard-of-care. We propose a 'pay-it-forward' gonorrhea and chlamydia testing randomized controlled trial (PIONEER). The trial would evaluate the effectiveness of two pay-it-forward strategies in promoting testing uptake compared to the standard of care (in which men pay for their tests out-of-pocket) among MSM and male STD patients in China.
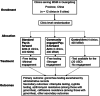
Methods: PIONEER will be a three-armed, pragmatic cluster randomized controlled trial (RCT), conducted across 12 clinics (six MSM-led and six public STD clinics) to compare the effectiveness of three implementation strategies. Each facility will be randomized to a standard pay-it-forward intervention of gonorrhea/ chlamydia testing with minimal encouragement for testing, a community-engaged pay-it-forward arm, or a control arm where men pay for their tests out-of-pockets. The primary outcome will be dual gonorrhea/chlamydia test uptake. Secondary outcomes will include syphilis testing, amount donated in pay-it-forward, number of positive gonorrhea and chlamydia tests, and measures of antimicrobial resistance. A sequential transformative mixed methods design will be used to evaluate the implementation process in type 2 effectiveness-implementation hybrid design. Data sources will include survey on acceptability, and feelings and attitudes towards the interventions among participants; testing and treatment uptake data from clinic records, WeChat records, and qualitative data to gain insights into men's perceptions and attitudes towards the pay-it-forward, mechanisms driving uptake, and donating behaviors. Implementers and organizers will be interviewed about fidelity and adherence to protocol, sustainability of pay-it-forward intervention, and barriers and facilitators of implementing the intervention.
Discussion: PIONEER will substantially increase gonorrhea/chlamydia testing among MSM in China, providing an innovative and new financial mechanism to sustain STD screening among sexual minorities in low- and middle-income countries. This study will answer compelling scientific questions about how best to implement pay-it-forward and the individual and organizational characteristics that moderate it.
Trial registration: The study with identification number NCT05723263 has been registered on clinicaltrials.gov/.
Keywords: Chlamydia; Gonorrhea; Pay-it-forward; Social innovation; Upstream reciprocity; Warm-glow.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
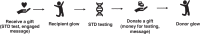
Similar articles
-
Pay-it-forward gonorrhea and chlamydia testing among men who have sex with men in China: a study protocol for a three-arm cluster randomized controlled trial.Infect Dis Poverty. 2019 Aug 16;8(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s40249-019-0581-1. Infect Dis Poverty. 2019. PMID: 31426869 Free PMC article.
-
Pay-it-forward strategy to enhance uptake of dual gonorrhea and chlamydia testing among men who have sex with men in China: a pragmatic, quasi-experimental study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 Jan;19(1):76-82. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30556-5. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30587296 Free PMC article.
-
Pay-it-forward gonorrhoea and chlamydia testing among men who have sex with men in China: a randomised controlled trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Aug;20(8):976-982. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30172-9. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32530426 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Infections: A Review.JAMA. 2022 Jan 11;327(2):161-172. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.23487. JAMA. 2022. PMID: 35015033 Review.
-
Non-conventional interventions to prevent gonorrhea or syphilis among men who have sex with men: A scoping review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 20;9:952476. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.952476. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36203757 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A pay-it-forward approach to improve feedback rate of HPV-based self-sampling in cervical cancer screening among women in ethnic minority regions of China: a randomized controlled trial protocol.Front Psychiatry. 2025 May 29;16:1586076. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1586076. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40511463 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of pay it forward intervention compared to free and user-paid vaccinations on seasonal influenza vaccination among older adults across seven cities in China: study protocol of a three-arm cluster randomized controlled trial.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):2372. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23301-2. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40610910 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting caregivers' HPV vaccination decisions for adolescent girls: A secondary analysis of a Chinese RCT.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 17;20(6):e0324260. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324260. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40526724 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sociodemographic characteristics, community engagement and stigma among Men who have Sex with Men (MSM) who attend MSM-led versus public sexual health clinics: A cross-sectional survey in China.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 16;19(10):e0310957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310957. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39413097 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

