Oridonin promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress via TP53-repressed TCF4 transactivation in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 37337284
- PMCID: PMC10278272
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02702-4
Oridonin promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress via TP53-repressed TCF4 transactivation in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: The incidence of colorectal cancer and cancer death rate are increasing every year, and the affected population is becoming younger. Traditional Chinese medicine therapy has a unique effect in prolonging survival time and improving the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer. Oridonin has been reported to have anti-cancer effects in a variety of tumors, but the exact mechanism remains to be investigated.
Methods: Cell Counting Kit-8 assay (CCK8) and 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) staining assay, Tranwell, and Wound healing assays were performed to measure cell proliferation, invasion, and migration capacities, respectively. The protein and mRNA expression levels of various molecules were reflected by Western blot and Reverse Transcription quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR). Transcription Factor 4 (TCF4) and its target genes were analyzed by Position Weight Matrices (PWMs) software and the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Immunofluorescence (IF) was performed to visualize the expression and position of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) stress biomarkers. The morphology of the ER was demonstrated by the ER tracker-red. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) levels were measured using a flow cytometer (FCM) or fluorescent staining. Calcium ion (Ca2+) concentration was quantified by Fluo-3 AM staining. Athymic nude mice were modeled with subcutaneous xenografts.
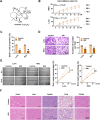
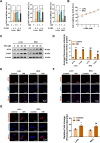
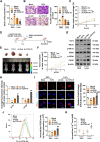
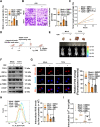
Results: Oridonin inhibited the proliferation, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer, and this effect was weakened in a concentration-dependent manner by ER stress inhibitors. In addition, oridonin-induced colorectal tumor cells showed increased expression of ER stress biomarkers, loose morphology of ER, increased vesicles, and irregular shape. TCF4 was identified as a regulator of ER stress by PWMs software and GEO survival analysis. In vitro and in vivo experiments confirmed that TCF4 inhibited ER stress, reduced ROS production, and maintained Ca2+ homeostasis. In addition, oridonin also activated TP53 and inhibited TCF4 transactivation, further exacerbating the elevated ROS levels and calcium ion release in tumor cells and inhibiting tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer cells in vivo.
Conclusions: Oridonin upregulated TP53, inhibited TCF4 transactivation, and induced ER stress dysregulation in tumor cells, promoting colorectal cancer cell death. Therefore, TCF4 may be one of the important nodes for tumor cells to regulate ER stress and maintain protein synthesis homeostasis. And the inhibition of the TP53/TCF4 axis plays a key role in the anti-cancer effects of oridonin.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Oridonin; Transcription factor 4; Tumor protein p53.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Insights from Traditional Chinese Medicine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;17(12):1599. doi: 10.3390/ph17121599. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXD3, frequently methylated in colorectal cancer, acts as a tumor suppressor and induces tumor cell apoptosis under ER stress via p53.Carcinogenesis. 2020 Sep 24;41(9):1253-1262. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz198. Carcinogenesis. 2020. PMID: 31784734
-
Curcumin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated apoptosis in human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells via disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jun;97(24):e11095. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011095. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29901626 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oridonin induces apoptosis and senescence in colorectal cancer cells by increasing histone hyperacetylation and regulation of p16, p21, p27 and c-myc.BMC Cancer. 2010 Nov 6;10:610. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-610. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21054888 Free PMC article.
-
Scoulerine promotes cell viability reduction and apoptosis by activating ROS-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress in colorectal cancer cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Aug 25;327:109184. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109184. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 32590070
Cited by
-
The dual effect of endoplasmic reticulum stress in digestive system tumors and intervention of Chinese botanical drug extracts: a review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 21;15:1339146. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1339146. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38449811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing cancer therapy: advanced nanovehicle delivery systems for oridonin.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 3;15:1476739. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1476739. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39691396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of colorectal cancer by traditional Chinese medicine: prevention and treatment mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 9;15:1377592. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1377592. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38783955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Insights from Traditional Chinese Medicine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;17(12):1599. doi: 10.3390/ph17121599. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oridonin-induced ferroptosis and apoptosis: a dual approach to suppress the growth of osteosarcoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 12;24(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11951-1. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38347435 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

