A Case of Antisynthetase Syndrome in the Setting of SARS-Cov-2 Infection
- PMID: 37337554
- PMCID: PMC10277010
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.40588
A Case of Antisynthetase Syndrome in the Setting of SARS-Cov-2 Infection
Abstract
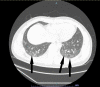
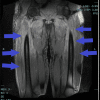
Antisynthetase syndrome is a complex autoimmune disorder, and one of the key criteria for diagnosis is the presence of myositis. Additionally, evidence of interstitial lung disease (ILD) is another important indicator for diagnosis; other clinical features associated with antisynthetase syndrome include arthritis, unexplained and persistent fever, Raynaud's phenomenon, and the presence of mechanic's hands. We report a case of a 36-year-old male who presented to the emergency department with shortness of breath and proximal muscle weakness in the setting of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-Cov-2) infection, as his inflammatory markers were elevated and he exhibited features suspicious for antisynthetase syndrome, he was started on methylprednisolone 40 mg intravenously every eight hours, and a myositis panel was checked. In addition, a chest computed tomography (CT) exhibited ground-glass opacities which were compatible with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). A magnetic resonance image (MRI) of both thighs was done, revealing significant swelling and confirming the suspicion of myositis as his muscle strength in his lower extremities took significant time to improve. As days passed, his muscle strength improved significantly and his creatine phosphatase kinase (CPK) values trended down, indicating that his myositis was improving as well. He was transitioned to oral prednisone 60 mg daily and was discharged home with a rheumatology follow-up to define long-term treatment. A myositis panel revealed anti-glycyl-transferRNA synthetase (EJ) autoantibody positivity and a diagnosis was established. Our case revealed how sometimes laboratory values do not necessarily correlate with disease severity and how we have to do a thorough history of present illness and physical exam to think about unusual diagnoses before putting laboratory data into context.
Keywords: anti synthetase syndrome; anti-ej antibody; anti-jo-1 antibodies; inflammatory myositis; mechanic hands.
Copyright © 2023, Peña et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
