Weighted multiple testing procedures in genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 37337586
- PMCID: PMC10276986
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15369
Weighted multiple testing procedures in genome-wide association studies
Abstract
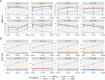
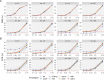
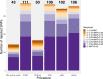
Multiple testing procedures controlling the false discovery rate (FDR) are increasingly used in the context of genome wide association studies (GWAS), and weighted multiple testing procedures that incorporate covariate information are efficient to improve the power to detect associations. In this work, we evaluate some recent weighted multiple testing procedures in the specific context of GWAS through a simulation study. We also present a new efficient procedure called wBHa that prioritizes the detection of genetic variants with low minor allele frequencies while maximizing the overall detection power. The results indicate good performance of our procedure compared to other weighted multiple testing procedures. In particular, in all simulated settings, wBHa tends to outperform other procedures in detecting rare variants while maintaining good overall power. The use of the different procedures is illustrated with a real dataset.
Keywords: False discovery rate; Genome wide association studies; Weighted MTP.
©2023 Obry et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
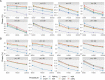
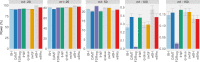
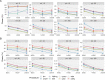
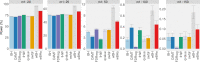
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological) 1995;57:289–300. doi: 10.1111/J.2517-6161.1995.TB02031.X. - DOI
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Multiple hypotheses testing with weights. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics. 1997;24:407–418. doi: 10.1111/1467-9469.00072. - DOI
-
- Benjamini Y, Krieger AM, Yekutieli D. Adaptive linear step-up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika. 2006;93:491–507. doi: 10.1093/BIOMET/93.3.491. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

