State-of-the-Art in the Drug Discovery Pathway for Chagas Disease: A Framework for Drug Development and Target Validation
- PMID: 37337597
- PMCID: PMC10277022
- DOI: 10.2147/RRTM.S415273
State-of-the-Art in the Drug Discovery Pathway for Chagas Disease: A Framework for Drug Development and Target Validation
Abstract
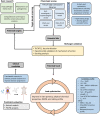
Chagas disease is the most important protozoan infection in the Americas, and constitutes a significant public health concern throughout the world. Development of new medications against its etiologic agent, Trypanosoma cruzi, has been traditionally slow and difficult, lagging in comparison with diseases caused by other kinetoplastid parasites. Among the factors that explain this are the incompletely understood mechanisms of pathogenesis of T. cruzi infection and its complex set of interactions with the host in the chronic stage of the disease. These demand the performance of a variety of in vitro and in vivo assays as part of any drug development effort. In this review, we discuss recent breakthroughs in the understanding of the parasite's life cycle and their implications in the search for new chemotherapeutics. For this, we present a framework to guide drug discovery efforts against Chagas disease, considering state-of-the-art preclinical models and recently developed tools for the identification and validation of molecular targets.
Keywords: Chagas disease; Trypanosoma cruzi; animal models; drug development; screenings; target.
© 2023 Gabaldón-Figueira et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources