Suppression of cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling ameliorates retinal injury in diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 37338034
- PMCID: PMC11895893
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12722
Suppression of cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling ameliorates retinal injury in diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
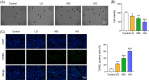
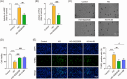
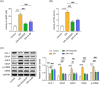
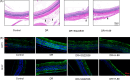
The blood-retinal barrier (BRB), homeostasis, neuronal integrity, and metabolic processes are all directly influenced by Müller cells, the most important retinal glial cells. We isolated primary Müller cells from Sprague-Dawley (SD) neonatal rats and treated them with glucose at varying doses. CCK-8 was used to quantify cellular viability, and a TUNEL assay was performed to detect cell apoptosis. ELISA, immunofluorescence, and western blotting were used to assess cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling, Kir4.1, AQP4, GFAP, and VEGF levels, respectively. H&E staining was used to examine histopathological alterations in diabetic retinopathy (DR)-affected retinal tissue in rats. As glucose concentration increases, gliosis of Müller cells became apparent, as evidenced by a decline in cell activity, an increase in apoptosis, downregulation of Kir4.1 level, and overexpression of GFAP, AQP4, and VEGF. Treatments with low, intermediate, and high glucose levels led to aberrant activation of cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling. Interestingly, blocking cAMP and PKA reduced high glucose-induced Müller cell damage and gliosis by a significant amount. Further in vivo results suggested that cAMP or PKA inhibition significantly improved edema, bleeding, and retinal disorders. Our findings showed that high glucose exacerbated Müller cell damage and gliosis via a mechanism involving cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling.
Keywords: Müller cells; cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling; diabetic retinopathy.
© 2023 The Authors. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Thomas MC. The clustering of cardiovascular, renal, adipo‐metabolic eye and liver disease with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism. 2022;128:154961. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Lu X, Wei L, Ye D, Lin J, Tang X, et al. PHD2 attenuates high‐glucose‐induced blood retinal barrier breakdown in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells by regulating the Hif‐1alpha/VEGF pathway. Inflamm Res. 2022;71(1):69–79. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 21LC01003/Shanghai Eye Diseases Prevention and Treatment Center Support
- 18ZR1435600/the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai
- No.ZY(2021-2023)-0207-01-09/A three-year action plan for TCM inheritance, innovation and development
- SHDC12018X16/Technology innovation project of Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

