Complete Genome of Agrobacterium fabrum Strain 1D1416
- PMID: 37338417
- PMCID: PMC10353357
- DOI: 10.1128/mra.00264-23
Complete Genome of Agrobacterium fabrum Strain 1D1416
Abstract
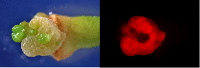
This work reports the draft genome of Agrobacterium fabrum strain 1D1416. The assembled genome is composed of a 2,837,379-bp circular chromosome, a 2,043,296-bp linear chromosome, a 519,735-bp AT1 plasmid, a 188,396-bp AT2 plasmid, and a 196,706-bp Ti virulence plasmid. The nondisarmed strain produces gall-like structures in citrus tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Qiagen. 2013–2023. CLC Genomics Workbench 8.5. Qiagen, Redwood City, CA. https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com/products-overview/discovery-insights-....
-
- Brettin T, Davis JJ, Disz T, Edwards RA, Gerdes S, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Overbeek R, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Shukla M, Thomason JA, III, Stevens R, Vonstein V, Wattam AR, Xia F. 2015. RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci Rep 5:8365. doi: 10.1038/srep08365. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
