Opioids for the management of dyspnea in cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37338727
- PMCID: PMC10390357
- DOI: 10.1007/s10147-023-02362-6
Opioids for the management of dyspnea in cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
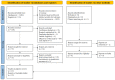
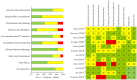
Dyspnea is a prevalent symptom that significantly reduces quality of life of cancer patients. Palliative treatment is necessary when the symptoms do not respond to treatment for their cause. Opioids are widely used as pharmacological therapy, but evidence for individual agents is inconsistent. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of opioids for dyspnea in cancer patients. We searched the CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and ICHUSHI for studies using opioids for dyspnea in adult cancer patients reported by September 2019. Screening of the retrieved literature and assessment of risk of bias and outcomes were performed by two independent authors. A meta-analysis was performed on the primary endpoint, relief of dyspnea, and secondary endpoints including quality of life, somnolence as a side effect, and serious adverse events. Twelve randomized controlled trials were evaluated regarding relief of dyspnea. Somnolence and serious adverse events were evaluated in seven and four randomized controlled trials, respectively, but no randomized controlled trials were evaluable for quality of life. Overall, opioids were more effective than placebo for dyspnea (standardized mean difference - 0.43, 95% confidence interval [CI] - 0.75 to - 0.12). Although significant difference was found between systemic morphine and placebo in the drug-specific analysis, no significant difference could be detected in the other analyses. Systemic administration of opioids is more effective than placebo in relieving dyspnea in cancer patients. Robust evidence on the efficacy and safety of opioids on dyspnea in cancer patients is lacking, and further studies are needed.
Keywords: Cancer; Dyspnea; Meta-analysis; Opioid; Systematic review.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TN received research grants from I&H Co., Ltd., Cocokarafine Co., Ltd. and Konica Minolta Inc., and honoraria from Pfizer Japan, Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Dentsu and Otsuka Pharmaceutical. Other authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures





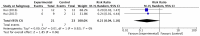

References
-
- Chan K, Tse DMW, Sham MMK. Oxford textbook of palliative medicine. 5. New York: Oxford University Press; 2015. Dyspnoea and other respiratory symptoms in palliative care; pp. 421–429.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

