FEV1/FVC Severity Stages for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 37339502
- PMCID: PMC10515563
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202303-0450OC
FEV1/FVC Severity Stages for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
Rationale: The diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is based on a low FEV1/FVC ratio, but the severity of COPD is classified using FEV1% predicted (ppFEV1). Objectives: To test a new severity classification scheme for COPD using FEV1/FVC ratio, a more robust measure of airflow obstruction than ppFEV1. Methods: In COPDGene (Genetic Epidemiology of COPD) (N = 10,132), the severity of airflow obstruction was categorized by Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) stages 1-4 (ppFEV1 of ⩾80%, ⩾50-80%, ⩾30-50%, and <30%). A new severity classification (STaging of Airflow obstruction by Ratio; STAR) was tested in COPDGene-FEV1/FVC ⩾0.60 to <0.70, ⩾0.50 to <0.60, ⩾0.40 to <0.50, and <0.40, respectively, for stages 1-4-and applied to the combined Pittsburgh SCCOR and Emphysema COPD Research Registry for replication (N = 2,017). Measurements and Main Results: The agreements (weighted Bangdiwala B values) between GOLD and the new FEV1/FVC ratio severity stages were 0.89 in COPDGene and 0.88 in the Pittsburgh cohort. In COPDGene and the Pittsburgh cohort, compared with GOLD staging, STAR provided significant discrimination between the absence of airflow obstruction and stage 1 for all-cause mortality, respiratory quality of life, dyspnea, airway wall thickness, exacerbations, and lung function decline. No major differences were noted for emphysema, small airway disease, and 6-minute-walk distance. The STAR classification system identified a greater number of adults with stage 3/4 disease who would be eligible for lung transplantation and lung volume reduction procedure evaluations. Conclusions: The new STAR severity classification scheme provides discrimination for mortality that is similar to the GOLD classification but with a more uniform gradation of disease severity. STAR differentiates patients' symptoms, disease burden, and prognosis better than the existing scheme based on ppFEV1, and is less sensitive to race/ethnicity and other demographic characteristics.
Keywords: COPD; airflow obstruction; severity; staging.
Figures
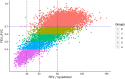

Comment in
-
A STAR Is Born: A New Approach to Assessing Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Severity.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023 Sep 15;208(6):647-648. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202306-1106ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 37486264 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Novel FEV1/FVC-based Diagnosis and Severity Classification of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: How about FEV1 % Predicted Basing?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Feb 1;209(3):340-341. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202310-1739LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38033312 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Use FEV1/FVC Z-Score Staging to Minimize Sex and Age Bias in Staging Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Feb 1;209(3):341-342. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202310-1761LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38033313 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is This Really a New START in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Feb 1;209(3):339-340. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202309-1709LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38033314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Stanojevic S, Kaminsky DA, Miller MR, Thompson B, Aliverti A, Barjaktarevic I, et al. ERS/ATS technical standard on interpretive strategies for routine lung function tests. Eur Respir J . 2022;60:2101499. - PubMed
-
- Elmaleh-Sachs A, Balte P, Oelsner EC, Allen NB, Baugh A, Bertoni AG, et al. Race/ethnicity, spirometry reference equations, and prediction of incident clinical events: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) lung study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2022;205:700–710. - PubMed
-
- McCormack MC, Balasubramanian A, Matsui EC, Peng RD, Wise RA, Keet CA. Race, lung function, and long-term mortality in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2022;205:723–724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

