Pangolin-inspired untethered magnetic robot for on-demand biomedical heating applications
- PMID: 37339969
- PMCID: PMC10282021
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-38689-x
Pangolin-inspired untethered magnetic robot for on-demand biomedical heating applications
Abstract
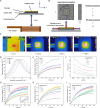
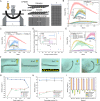
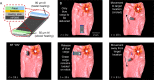
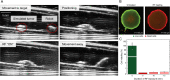
Untethered magnetic miniature soft robots capable of accessing hard-to-reach regions can enable safe, disruptive, and minimally invasive medical procedures. However, the soft body limits the integration of non-magnetic external stimuli sources on the robot, thereby restricting the functionalities of such robots. One such functionality is localised heat generation, which requires solid metallic materials for increased efficiency. Yet, using these materials compromises the compliance and safety of using soft robots. To overcome these competing requirements, we propose a pangolin-inspired bi-layered soft robot design. We show that the reported design achieves heating > 70 °C at large distances > 5 cm within a short period of time <30 s, allowing users to realise on-demand localised heating in tandem with shape-morphing capabilities. We demonstrate advanced robotic functionalities, such as selective cargo release, in situ demagnetisation, hyperthermia and mitigation of bleeding, on tissue phantoms and ex vivo tissues.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
On-demand anchoring of wireless soft miniature robots on soft surfaces.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Aug 23;119(34):e2207767119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2207767119. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35969749 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Metal-Elastomer Composites with Dual-Energy Transmission Mode for Multifunctional Miniature Untethered Magnetic Robots.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Nov;9(31):e2203730. doi: 10.1002/advs.202203730. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 36065052 Free PMC article.
-
Untethered Miniature Tensegrity Robot with Tunable Stiffness for High-Speed and Adaptive Locomotion.Soft Robot. 2025 Apr 15. doi: 10.1089/soro.2024.0178. Online ahead of print. Soft Robot. 2025. PMID: 40233159
-
Magnetic Soft Materials and Robots.Chem Rev. 2022 Mar 9;122(5):5317-5364. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00481. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35104403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Biomedical applications of bionic untethered micro-nano robots].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Oct 25;38(5):1003-1009. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202006022. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34713669 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Untethered Microgrippers for Biopsy in the Upper Urinary Tract.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Nov;13(29):e2401407. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202401407. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 39101622
-
Advances in Magnetically Controlled Medical Robotics: A Review of Actuation Systems, Continuum Designs, and Clinical Prospects for Minimally Invasive Therapies.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 May 6;16(5):561. doi: 10.3390/mi16050561. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Numerical simulation and mathematical modeling of biomechanical stress distribution in poroelastic tumor tissue via magnetic field and bio-ferro-fluid.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 15;10(14):e34651. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34651. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39149009 Free PMC article.
-
Wireless Magnetic Robot for Precise Hierarchical Control of Tissue Deformation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(35):e2308619. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308619. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39041885 Free PMC article.
-
Four-Dimensional-Printed Microrobots and Their Applications: A Review.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Aug 15;14(8):1607. doi: 10.3390/mi14081607. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37630143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cianchetti M, Laschi C, Menciassi A, Dario P. Biomedical applications of soft robotics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018;3:143–153. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0022-y. - DOI
-
- M. Sitti, Mobile Microrobotics. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 2017. https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/mobile-microrobotics).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

