Prognostic impact of blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio on patients with sepsis: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 37340147
- PMCID: PMC10282077
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-37127-8
Prognostic impact of blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio on patients with sepsis: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
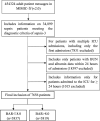
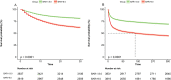
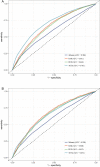
To investigate the ability of the ratio of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) to serum albumin ratio (BAR) in patients with sepsis in intensive care units (ICUs) to predict the prognosis of short-and long-term death. Data are from the Marketplace for Intensive Care Medical Information IV (MIMIC-IV v2.0) database for patients with sepsis as defined by SEPSIS-3. The primary outcome was 30-day mortality and the secondary outcome was 360-day mortality. Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival curves were plotted to describe differences in BAR mortality in different subgroups and area under the curve (AUC) analysis was performed to compare the predictive value of sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA), BAR, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and albumin. Multivariate Cox regression models and subgroup analysis were used to determine the correlation between BAR and 30-day mortality and 360-day mortality. A total of 7656 eligible patients were enrolled in the study with a median BAR of 8.0 mg/g, including 3837 in the ≤ 8.0 group and 3819 in the BAR > 8.0 group, with 30-day mortality rates of 19.1% and 38.2% (P < 0.001) and 360-day mortality rates of 31.1% and 55.6% (P < 0.001). Multivariate Cox regression models showed an increased risk of death for 30-day mortality (HR = 1.219, 95% CI 1.095-1.357; P < 0.001) and 360-day mortality (HR = 1.263, 95% CI 1.159-1.376; P < 0.001) in the high BAR group compared to the low BAR group. For the 30-day outcome, the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.661 for BAR and 0.668 for 360-day BAR. In the subgroup analysis, BAR remained an isolated risk factor for patient death. As a clinically inexpensive and readily available parameter, BAR can be a valuable forecaster of prognosis in patients with sepsis in the intensive care unit.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio with mortality in acute pancreatitis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 17;15(1):13327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97891-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40247063 Free PMC article.
-
Blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio as predictor of mortality among acute pancreatitis patients in ICU: A retrospective cohort study.PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0323321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323321. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40373080 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio in septic patients with acute kidney injury-a retrospective study based on MIMIC database.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 7;12:1510919. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1510919. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40400629 Free PMC article.
-
Blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio is associated with all-cause mortality in patients with AKI: a cohort study.Front Nutr. 2024 Feb 20;11:1353956. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1353956. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38445205 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio and all-cause mortality in critical ill acute ischemic stroke patients: a retrospective cohort study of MIMIC-IV database 3.0.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 7;11:1509284. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1509284. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39839282 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Deep learning-based prediction of in-hospital mortality for sepsis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):372. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49890-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38172160 Free PMC article.
-
Association of blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio with mortality in acute pancreatitis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 17;15(1):13327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97891-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40247063 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio and cardiovascular diseases, cardiovascular mortality, and all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 11;16:1456731. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1456731. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40290308 Free PMC article.
-
Blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio as predictor of mortality among acute pancreatitis patients in ICU: A retrospective cohort study.PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0323321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323321. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40373080 Free PMC article.
-
Association between blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio and 28-day mortality in ICU patients with acute respiratory failure: a retrospective analysis of MIMIC-IV database.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025 Jul 6;25(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12911-025-03100-w. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025. PMID: 40619355 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

