The correlation of hemoglobin and 28-day mortality in septic patients: secondary data mining using the MIMIC-IV database
- PMID: 37340360
- PMCID: PMC10280861
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-023-08384-9
The correlation of hemoglobin and 28-day mortality in septic patients: secondary data mining using the MIMIC-IV database
Abstract
Background: Previous studies found minimal evidence and raised controversy about the link between hemoglobin and 28-day mortality in sepsis patients. As a result, the purpose of this study was to examine the association between hemoglobin and 28-day death in sepsis patients by analyzing the Medical Intensive Care IV (MIMIC-IV) database from 2008 to 2019 at an advanced medical center in Boston, Massachusetts.
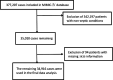
Methods: We extracted 34,916 sepsis patients from the MIMIC-IV retrospective cohort database, using hemoglobin as the exposure variable and 28-day death as the outcome variable, and after adjusting for confounders (demographic indicators, Charlson co-morbidity index, SOFA score, vital signs, medication use status (glucocorticoids, vasoactive drugs, antibiotics, and immunoglobulins, etc.)), we investigated the independent effects of hemoglobin and 28-day risk of death by binary logistic regression as well as two-piecewise linear model, respectively.
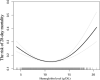
Results: Hemoglobin levels and 28-day mortality were shown to be non-linearly related.The inflection points were 104 g/L and 128 g/L, respectively. When HGB levels were between 41 and 104 g/L, there was a 10% decrease in the risk of 28-day mortality (OR: 0.90; 95% CI: 0.87 to 0.94, p-value = 0.0001). However, in the range of 104-128 g/L, we did not observe a significant association between hemoglobin and 28-day mortality (OR: 1.17; 95% CI: 1.00 to 1.35, P value = 0.0586). When HGB was in the range of 128-207 g/L, there was a 7% increase in the risk of 28-day mortality for every 1 unit increase in HGB (OR: 1.07; 95% CI: 1.01 to 1.15, P value = 0.0424).
Conclusion: In patients with sepsis, baseline hemoglobin was related to a U-shaped risk of 28-day death. When HGB was in the range of 12.8-20.7 g/dL, there was a 7% increase in the risk of 28-day mortality for every 1 unit increase in HGB.
Keywords: Hemoglobin; MIMIC-IV; Retrospective study; sepsis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between hemoglobin and in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with sepsis: evidence from two large databases.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Dec 19;24(1):1450. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10335-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39702030 Free PMC article.
-
[A nonlinear relationship between the hemoglobin level and prognosis of elderly patients with sepsis: an analysis based on MIMIC-IV].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Jun;35(6):573-577. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20221009-00900. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37366121 Chinese.
-
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient nonlinearly impacts the 28-day mortality of patients with sepsis: Secondary data mining based on the MIMIC-IV database.Clin Respir J. 2023 May;17(5):447-455. doi: 10.1111/crj.13614. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37076114 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the magnitude of haemoglobin changes and long-term mortality in patients with sepsis: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jun 11;24(1):577. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09476-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38862875 Free PMC article.
-
Association between base excess and 28-day mortality in sepsis patients: A secondary analysis based on the MIMIC- IV database.Heliyon. 2023 May 9;9(5):e15990. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15990. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37215834 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and performance evaluation of a clinical prediction model for sepsis risk in burn patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 29;103(48):e40709. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040709. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39612449 Free PMC article.
-
Hemoglobin, Ferritin, and Lactate Dehydrogenase as Predictive Markers for Neonatal Sepsis.J Pers Med. 2024 Apr 29;14(5):476. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050476. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793057 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and Risk Factors for Pediatric Sepsis.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Jun;44(3):648-656. doi: 10.1007/s11596-024-2870-6. Epub 2024 May 15. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38748371
-
Association between hemoglobin and in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with sepsis: evidence from two large databases.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Dec 19;24(1):1450. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10335-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39702030 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between sepsis occurrence, hemoglobin level and mortality in patients with non-trauma hemorrhagic brain injuries: trajectory-based analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Mar 6;30(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02417-6. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40051005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315(8):801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Effenberger-Neidnicht K, Hartmann M. Mechanisms of Hemolysis during Sepsis. Inflammation. 2018 Oct;41(5):1569–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021-GMHCT-007/2021 hospital-level clinical research project of Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University (2021-GMHCT-007):Development and external validation of a 28-day mortality risk prediction model for sepsis patients based on machine learning algorithms
- gzwkj-2022-018/Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission (gzwkj-2022-018) :Construction of a sepsis specific disease cohort database
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials