Association of serum uric acid with hepatic steatosis detected by controlled attenuation parameter in the United States population
- PMID: 37340407
- PMCID: PMC10280954
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-023-01846-8
Association of serum uric acid with hepatic steatosis detected by controlled attenuation parameter in the United States population
Abstract
Background: The relationship between serum uric acid (SUA) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been previously reported. Controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) has better diagnostic performance than ultrasonography for assessing hepatic steatosis. The association of SUA with hepatic steatosis detected by CAP is worth further study.
Methods: The US population aged 20 years or older from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) was assessed. Hepatic steatosis was evaluated by the controlled attenuation parameter (CAP). NAFLD status was defined as CAP values of 268 dB/m without hepatitis B or C virus infection or considerable alcohol consumption. Multiple imputations were performed to fill in the missing covariate values. Linear regression, logistic regression, and smooth curve fitting were used to examine the association.
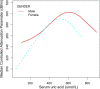
Results: In total, 3919 individuals participated in this study. There was a positive association between SUA (µmol/L) and CAP (β = 0.14, 95% CI: 0.12-0.17, P < 0.01). After stratification by sex, a significant relationship between SUA and CAP existed in both males (β = 0.12, 95% CI: 0.09-0.16, P < 0.01) and females (β = 0.17, 95% CI: 0.14-0.20, P < 0.01) after multiple imputation. The inflection points of the threshold effect of SUA on CAP were 487.7 µmol/L in males and 386.6 µmol/L in females. There was a positive association between SUA (mg/dL) and NAFLD (OR = 1.30, 95% CI: 1.23-1.37, P < 0.01). After stratification by race, positive relationships were also observed. Meanwhile, a positive relationship existed between hyperuricemia and NAFLD (OR = 1.94, 95% CI: 1.64-2.30, P < 0.01). The positive relationship was more significant in females than in males (P for interaction < 0.01).
Conclusions: There was a positive association between SUA and CAP, as well as between SUA and NAFLD. Subgroup studies stratified by sex and ethnicity demonstrated that the effects were consistent.
Keywords: A cross-sectional study; Controlled attenuation parameter; NHANES; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Serum uric acid.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum uric acid to creatinine ratio is associated with higher prevalence of NAFLD detected by FibroScan in the United States.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Aug;36(8):e24590. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24590. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35808891 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between serum uric acid levels and hepatic steatosis in non-obese postmenopausal women.Climacteric. 2014 Dec;17(6):692-9. doi: 10.3109/13697137.2014.926323. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Climacteric. 2014. PMID: 24884478
-
Association between serum uric acid-to-creatinine ratio and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study in Chinese non-obese people with a normal range of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 14;22(1):419. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02500-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36104672 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter as a noninvasive test for steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2021 Oct;48(4):471-480. doi: 10.1007/s10396-021-01123-0. Epub 2021 Aug 20. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2021. PMID: 34415481 Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) as a non-invasive test for steatosis in suspected non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 8;19(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-0961-9. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30961539 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference (TyG_WC) in predicting metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease among individuals with hyperuricemia.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 4;25(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03786-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40186129 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of gender on survival outcomes in patients with small intestinal stromal tumors: a comprehensive analysis using the SEER database.Surg Endosc. 2024 Jul;38(7):3905-3916. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-10942-4. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38831215
-
Allopurinol versus Febuxostat: A New Approach for the Management of Hepatic Steatosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 16;11(11):3074. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113074. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38002074 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

