Oral ellagic acid attenuated LPS-induced neuroinflammation in rat brain: MEK1 interaction and M2 microglial polarization
- PMID: 37340785
- PMCID: PMC10350794
- DOI: 10.1177/15353702231182230
Oral ellagic acid attenuated LPS-induced neuroinflammation in rat brain: MEK1 interaction and M2 microglial polarization
Abstract
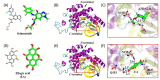
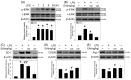
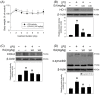
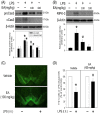
Ellagic acid, the marker component of peels of Punica granatum L., is known traditionally to treat traumatic hemorrhage. In this study, the cellular mechanism underlying ellagic acid-induced anti-inflammation was investigated using lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) as a neuroinflammation inducer. Our in vitro data showed that LPS (1 μg/mL) consistently phosphorylated ERK and induced neuroinflammation, such as elevation in tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and nitric oxide production in treated BV-2 cells. Incubation of ellagic acid significantly inhibited LPS-induced ERK phosphorylation and subsequent neuroinflammation in treated BV-2 cells. Furthermore, our in vivo study of neuroinflammation employed an intranigral infusion of LPS that resulted in a time-dependent elevation in phosphorylated ERK levels in the infused substantia nigra (SN). Oral administration of ellagic acid (100 mg/kg) significantly attenuated LPS-induced ERK phosphorylation. A four-day treatment of ellagic acid did not alter LPS-induced ED-1 elevation but ameliorated LPS-induced reduction in CD206 and arginase-1 (two biomarkers of M2 microglia). A seven-day treatment of ellagic acid abolished LPS-induced increases in heme-oxygenase-1, cyclo-oxygenase 2, and α-synuclein trimer levels (a pathological hallmark) in the infused SN. At the same time, ellagic acid attenuated LPS-induced increases in active caspase 3 and receptor-interacting protein kinase-3 levels (respective biomarkers of apoptosis and necroptosis) as well as reduction in tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells in the infused SN. In silico analysis showed that ellagic acid binds to the catalytic site of MEK1. Our data suggest that ellagic acid is capable of inhibiting MEK1-ERK signaling and then attenuated LPS-induced neuroinflammation, protein aggregation, and programmed cell deaths. Moreover, M2 microglial polarization is suggested as a novel antineuroinflammatory mechanism in the ellagic acid-induced neuroprotection.
Keywords: Ellagic acid; M2 microglial polarization; MEK-1; in silico assay; neuroinflammation; selumetinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gallic Acid Attenuated LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation: Protein Aggregation and Necroptosis.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jan;57(1):96-104. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01759-7. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31832973
-
Anti-inflammatory Effect of AZD6244 on Acrolein-Induced Neuroinflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jan;57(1):88-95. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01758-8. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31786775
-
Dexmedetomidine Inhibits Neuroinflammation by Altering Microglial M1/M2 Polarization Through MAPK/ERK Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2020 Feb;45(2):345-353. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02922-1. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 31823113
-
The Mycobacterial Adjuvant Analogue TDB Attenuates Neuroinflammation via Mincle-Independent PLC-γ1/PKC/ERK Signaling and Microglial Polarization.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Feb;56(2):1167-1187. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1135-4. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 29876879
-
Ellagic Acid Protects Dopamine Neurons via Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglia.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Nov 19;2020:2963540. doi: 10.1155/2020/2963540. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33294118 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oral administration of ellagic acid mitigates perioperative neurocognitive disorders, hippocampal oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation in aged mice by restoring IGF-1 signaling.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 30;14(1):2509. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53127-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38291199 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Assessment of the Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Polyphenols Against Tau Phosphorylation, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidative Stress.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 28;16(21):3667. doi: 10.3390/nu16213667. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519499 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical constituent characterization and determination of Quisqualis fructus based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and HPLC combined with fingerprint and chemometric analysis.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jun 21;15:1418480. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1418480. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38988635 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Bleomycin-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Intratracheal Instillation Administration of Ellagic Acid-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Mar 26;26(4):94. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03086-8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40140157
References
-
- Tejera D, Heneka MT. Microglia in neurodegenerative disorders. Methods Mol Biol 2019;2034:57–67 - PubMed
-
- Khatri N, Thakur M, Pareek V, Kumar S, Sharma S, Datusalia AK. Oxidative stress: major threat in traumatic brain injury. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2018;17:689–95 - PubMed
-
- Sasaki A. Microglia and brain macrophages: an update. Neuropathology 2017;37:452–64 - PubMed
-
- Lin AM, Wu LY, Hung KC, Huang HJ, Lei YP, Lu WC, Hwang LS. Neuroprotective effects of longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) flower water extract on MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in rat brain. J Agric Food Chem 2012;60:9188–94 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

