Structural polymorphism of the PH domain in TFIIH
- PMID: 37340985
- PMCID: PMC10345426
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20230846
Structural polymorphism of the PH domain in TFIIH
Abstract
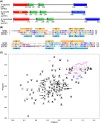
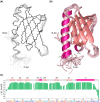
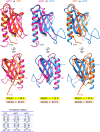
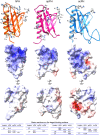
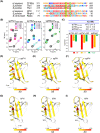
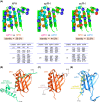
The general transcription factor TFIIH is a multi-subunit complex involved in transcription, DNA repair, and cell cycle in eukaryotes. In the human p62 subunit and the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Tfb1 subunit of TFIIH, the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain (hPH/scPH) recruits TFIIH to transcription-start and DNA-damage sites by interacting with an acidic intrinsically disordered region in transcription and repair factors. Whereas metazoan PH domains are highly conserved and adopt a similar structure, fungal PH domains are divergent and only the scPH structure is available. Here, we have determined the structure of the PH domain from Tfb1 of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe (spPH) by NMR. spPH holds an architecture, including the core and external backbone structures, that is closer to hPH than to scPH despite having higher amino acid sequence identity to scPH. In addition, the predicted target-binding site of spPH shares more amino acid similarity with scPH, but spPH contains several key residues identified in hPH as required for specific binding. Using chemical shift perturbation, we have identified binding modes of spPH to spTfa1, a homologue of hTFIIEα, and to spRhp41, a homologue of the repair factors hXPC and scRad4. Both spTfa1 and spRhp41 bind to a similar but distinct surface of spPH by modes that differ from those of target proteins binding to hPH and scPH, revealing that the PH domain of TFIIH interacts with its target proteins in a polymorphic manner in Metazoa, and budding and fission yeasts.
Keywords: NMR spectroscopy; PH domain; TFIIH; budding yeast; general transcription factor.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

