Cytoreductive prostatectomy may improve oncological outcomes in patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37341004
- PMCID: PMC10172051
- DOI: 10.4111/icu.20230058
Cytoreductive prostatectomy may improve oncological outcomes in patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
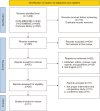
The oncologic outcomes of cytoreductive prostatectomy (CRP) in oligometastatic prostate cancer (OmPCa) are still controversial. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis on the oncologic outcome of CRP in OmPCa. OVID-Medline, OVID-Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were searched to identify eligible studies published before January 2023. A total of 11 studies (929 patients), 1 randomized controlled trial (RCT) and 10 non-RCT studies, were included in the final analysis. RCT and non-RCT were further analyzed separately. End points were progression-free-survival (PFS), time to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPCa), cancer-specific-survival (CSS) and overall-survival (OS). It was analyzed using hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). In PFS, in RCT, HR=0.43 (CIs=0.27-0.69) was shown statistically significant, but in non-RCTs, HR=0.50 (CIs=0.20-1.25), there was no statistical difference. And, in time to CRPCa was statistically significant in the CRP group in all analyses (RCT; HR=0.44; CIs=0.29-0.67) (non-RCTs; HR=0.64; CIs=0.47-0.88). Next, CSS was not statistically different between the two groups (HR=0.63; CIs=0.37-1.05). Finally, OS showed better results in the CRP group in all analyses (RCT; HR=0.44; CIs=0.26-0.76) (non-RCTs; HR=0.59; CIs=0.37-0.93). Patients who received CRP in OmPCa showed better oncologic outcomes compared to controls. Notably, time to CRPC and OS showed significantly improved compared with control. We recommend that experienced urologists who are capable of managing complications consider CRP as a strategy to achieve good oncological outcomes in OmPCa. However, since most of the included studies are non-RCT studies, caution should be exercised in interpreting the results.
Keywords: Cytoreduction surgical procedures; Neoplasm metastasis; Prostatectomy; Prostatic neoplasms; Radiotherapy.
© The Korean Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:8–10. - PubMed
-
- Gillessen S, Attard G, Beer TM, Beltran H, Bossi A, Bristow R, et al. Management of patients with advanced prostate cancer: the report of the Advanced Prostate Cancer Consensus Conference APCCC 2017. Eur Urol. 2018;73:178–211. - PubMed
-
- Miller DA, Krasna MJ. Local therapy indications in the management of patients with oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25:611–620. - PubMed
-
- Nesbit EG, Donnelly ED, Strauss JB. Treatment strategies for oligometastatic breast cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021;22:94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous