Measurement of rat and human tissue optical properties for improving the optical detection and visualization of peripheral nerves
- PMID: 37342709
- PMCID: PMC10278628
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.488761
Measurement of rat and human tissue optical properties for improving the optical detection and visualization of peripheral nerves
Abstract
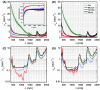
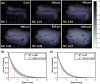
Peripheral nerve damage frequently occurs in challenging surgical cases resulting in high costs and morbidity. Various optical techniques have proven effective in detecting and visually enhancing nerves, demonstrating their translational potential for assisting in nerve-sparing medical procedures. However, there is limited data characterizing the optical properties of nerves in comparison to surrounding tissues, thus limiting the optimization of optical nerve detection systems. To address this gap, the absorption and scattering properties of rat and human nerve, muscle, fat, and tendon were determined from 352-2500 nm. The optical properties highlighted an ideal region in the shortwave infrared for detecting embedded nerves, which remains a significant challenge for optical approaches. A 1000-1700 nm hyperspectral diffuse reflectance imaging system was used to confirm these results and identify optimal wavelengths for nerve imaging contrast in an in vivo rat model. Optimal nerve visualization contrast was achieved using 1190/1100 nm ratiometric imaging and was sustained for nerves embedded under ≥600 µm of fat and muscle. Overall, the results provide valuable insights for optimizing the optical contrast of nerves, including those embedded in tissue, which could lead to improved surgical guidance and nerve-sparing outcomes.
© 2023 Optica Publishing Group under the terms of the Optica Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
JSB (F, I, P, E) is a Founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Yaya Scientific, LLC, which has a financial interest in the commercialization of nerve imaging technology developments. JSB, AMJ (P), and GT (P) have a patent pending on imaging-based detection of nerve that is related to the findings of this paper. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. All opinions presented in this manuscript belong to the authors alone, and not to any institutions to which they are affiliated with.
Figures




References
-
- Henningsen M. H., Jaeger P., Hilsted K. L., Dahl J. B., “Prevalence of saphenous nerve injury after adductor-canal-blockade in patients receiving total knee arthroplasty: Nerve injury and adductor-canal-blockade,” Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 57(1), 112–117 (2013). 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2012.02792.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stanford J. L., Feng Z., Hamilton A. S., Gilliland F. D., Stephenson R. A., Eley J. W., Albertsen P. C., Harlan L. C., Potosky A. L., “Urinary and Sexual Function After Radical Prostatectomy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: The Prostate Cancer Outcomes Study,” JAMA 283(3), 354 (2000). 10.1001/jama.283.3.354 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
