Burden, predictors, and outcome of unconsciousness among under-five children hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia: A retrospective study from a developing country
- PMID: 37343025
- PMCID: PMC10284379
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287054
Burden, predictors, and outcome of unconsciousness among under-five children hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia: A retrospective study from a developing country
Abstract
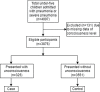
Despite the reduction of death from pneumonia over recent years, pneumonia has still been the leading infectious cause of death in under-five children for the last several decades. Unconsciousness is a critical condition in any child resulting from any illness. Once it occurs during a pneumonia episode, the outcome is perceived to be fatal. However, data on children under five with pneumonia having unconsciousness are scarce. We've retrospectively analyzed the data of under-five children admitted at the in-patient ward of Dhaka Hospital of icddr,b during 1 January 2014 and 31 December 2017 with World Health Organization classified pneumonia or severe pneumonia. Children presented with or without unconsciousness were considered as cases and controls respectively. Among a total of 3,876 children fulfilling the inclusion criteria, 325 and 3,551 were the cases and the controls respectively. A multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed older children (8 months vs. 7.9 months) (adjusted odds ratio, aOR 1.02, 95% CI: 1.004-1.04, p = 0.015), hypoxemia (aOR 3.22, 95% CI: 2.39-4.34, p<0.001), severe sepsis (aOR 4.46, 95% CI: 3.28-6.06, p<0.001), convulsion (aOR 8.90, 95% CI: 6.72-11.79, p<0.001), and dehydration (aOR 2.08, 95% CI: 1.56-2.76, p<0.001) were found to be independently associated with the cases. The cases more often had a fatal outcome than the controls (23% vs. 3%, OR 9.56, 95% CI: 6.95-13.19, p<0.001). If the simple predicting factors of unconsciousness in children under five hospitalized for pneumonia with different severity can be initially identified and adequately treated with prompt response, pneumonia-related deaths can be reduced more effectively, especially in resource-limited settings.
Copyright: © 2023 Mamun et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Gaston B. Pneumonia Pediatrics in review. 2002;23(4):132–40. - PubMed
-
- UNICEF, editor UNICEF Analysis Based on WHO and Maternal and Child Epidemiology Estimation Group Interim Estimates Produced in September 2019, Applying Cause Fractions for the Year 2017 to United Nations Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation Estimates for the Year 2018. Convention on the Rights of the Child; 2019.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical