Non-equilibrium Steady States in Catalysis, Molecular Motors, and Supramolecular Materials: Why Networks and Language Matter
- PMID: 37343130
- PMCID: PMC10326876
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c12665
Non-equilibrium Steady States in Catalysis, Molecular Motors, and Supramolecular Materials: Why Networks and Language Matter
Abstract
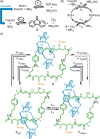
All chemists are familiar with the idea that, at equilibrium steady state, the relative concentrations of species present in a system are predicted by the corresponding equilibrium constants, which are related to the free energy differences between the system components. There is also no net flux between species, no matter how complicated the reaction network. Achieving and harnessing non-equilibrium steady states, by coupling a reaction network to a second spontaneous chemical process, has been the subject of work in several disciplines, including the operation of molecular motors, the assembly of supramolecular materials, and strategies in enantioselective catalysis. We juxtapose these linked fields to highlight their common features and challenges as well as some common misconceptions that may be serving to stymie progress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures







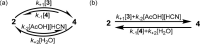

References
-
- Atkins P.; de Paula J.; Keeler J.. Atkins’ Physical Chemistry, 11th ed.; Oxford University Press, 2017.
-
- Wegscheider R. Über simultane Gleichgewichte und die Beziehungen zwischen Thermodynamik und Reactionskinetik homogener Systeme. Monatsh. Chem. Verwandte Teile Wissenschaften 1911, 32, 849–906. 10.1007/BF01517735. - DOI
- Onsager L. Reciprocal Relations in Irreversible Processes. I. Phys. Rev. 1931, 37, 405–426. 10.1103/PhysRev.37.405. - DOI
-
-
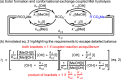
Although not typically higlighted in undergraduate chemistry, these relationships hold whether A and B are connected by a single, thermally accessible transition state or multiple pathways of direct exchange are important. k+/k– for any given pathway is always equal to Keq, and there is no net flux over any single pathway at equilibrium steady state, which is another statement of the principle of detailed balance.
-
-
- Maxwell J. C. IV. On the dynamical theory of gases. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. A 1867, 157, 49–88. 10.1098/rstl.1867.0004. - DOI
- Boltzmann L.Lectures on gas theory; University of California Press, Berkeley, CA, 1964.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

