A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of the Anti-Nerve Growth Factor Antibody Tanezumab in Subjects With Cancer Pain Due to Bone Metastasis
- PMID: 37343145
- PMCID: PMC10712717
- DOI: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad188
A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of the Anti-Nerve Growth Factor Antibody Tanezumab in Subjects With Cancer Pain Due to Bone Metastasis
Abstract
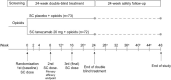
Background: This phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study assessed the efficacy and safety of tanezumab in subjects with cancer pain predominantly due to bone metastasis receiving background opioid therapy.
Methods: Subjects were randomized (stratified by (1) tumor aggressiveness and (2) presence/absence of concomitant anticancer treatment) to placebo or tanezumab 20 mg. Treatment was administered by subcutaneous injection every 8 weeks for 24 weeks (3 doses) followed by a 24-week safety follow-up period. The primary outcome was change in daily average pain in the index bone metastasis cancer pain site (from 0 = no pain to 10 = worst possible pain) from baseline to week 8.
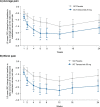
Results: LS mean (SE) change in pain at week 8 was -1.25 (0.35) for placebo (n = 73) and -2.03 (0.35) for tanezumab 20 mg (n = 72). LS mean (SE) [95% CI] difference from placebo was -0.78 (0.37) [-1.52, -0.04]; P = .0381 with α = 0.0478. The number of subjects with a treatment-emergent adverse event during the treatment period was 50 (68.5%) for placebo and 53 (73.6%) for tanezumab 20 mg. The number of subjects with a prespecified joint safety event was 0 for placebo and 2 (2.8%) for tanezumab 20 mg (pathologic fracture; n = 2).
Conclusion: Tanezumab 20 mg met the primary efficacy endpoint at week 8. Conclusions on longer-term efficacy are limited since the study was not designed to evaluate the durability of the effect beyond 8 weeks. Safety findings were consistent with adverse events expected in subjects with cancer pain due to bone metastasis and the known safety profile of tanezumab. Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT02609828.
Keywords: cancer pain; nerve growth factor; randomized controlled trial; tanezumab.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The study was sponsored by Pfizer and Eli Lilly and Company. Marie Fallon served as a study investigator for this trial and has served as an advisor to Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, and Fitabeo Therapeutics. Maciej Sopata served as a study investigator for this trial. Erika Dragon is a full-time employees of, and own stock and/or options in, Pfizer. Mark T. Brown was a full-time employee of Pfizer at the time the study was conducted and owns stock in Pfizer. Lars Viktrup is a full-time employee of, and owns stock in, Eli Lilly & Company. Christine R. West is a full-time employees of, and own stock and/or options in, Pfizer. Weihang Bao is a full-time employees of, and own stock and/or options in, Pfizer. Alex Agyemang is a full-time employees of, and own stock and/or options in, Pfizer. The study was sponsored by Pfizer and Eli Lilly and Company. Pfizer Inc and Eli Lily and Company contributed to the study design; Pfizer contributed to the management and collection of data. In their role as authors, employees of Pfizer and Eli Lilly were involved in the interpretation of data, preparation, review, and approval of the manuscript and the decision to submit for publication, along with their co-authors. The study sponsors approved the manuscript from an intellectual property perspective but had no right to veto the publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of tanezumab in the treatment of pain from bone metastases.Pain. 2015 Sep;156(9):1703-1713. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000211. Pain. 2015. PMID: 25919474 Clinical Trial.
-
Tanezumab for chronic low back pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, phase 3 study of efficacy and safety.Pain. 2020 Sep 1;161(9):2068-2078. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001928. Pain. 2020. PMID: 32453139 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Tanezumab on Joint Pain, Physical Function, and Patient Global Assessment of Osteoarthritis Among Patients With Osteoarthritis of the Hip or Knee: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2019 Jul 2;322(1):37-48. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.8044. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31265100 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of tanezumab administered as a fixed dosing regimen in patients with knee or hip osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled phase III trials.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Jun;40(6):2155-2165. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05488-4. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33159281 Review.
-
Relative Efficacy and Safety of Tanezumab for Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized-Controlled Trials.Clin J Pain. 2021 Dec 1;37(12):914-924. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000986. Clin J Pain. 2021. PMID: 34608021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Perineural dexamethasone effectively prolongs anaesthesic block duration in total hip arthroplasty, reduces opioid consumption, and does not compromise motor function, nerve integrity, or glycaemic control.Int Orthop. 2025 Aug;49(8):1791-1799. doi: 10.1007/s00264-025-06578-1. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Int Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40498110 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Influence of Anesthesia on Neuromonitoring During Scoliosis Surgery: A Systematic Review.NeuroSci. 2024 Dec 17;5(4):693-712. doi: 10.3390/neurosci5040049. NeuroSci. 2024. PMID: 39728681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel non-opioid analgesics in pain management.Pain Manag. 2024 Dec;14(12):641-651. doi: 10.1080/17581869.2024.2442292. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Pain Manag. 2024. PMID: 39692452 Review.
-
Focus on Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment.Curr Oncol. 2024 Jul 26;31(8):4241-4260. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31080316. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39195299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Invasion and metastasis in cancer: molecular insights and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Feb 21;10(1):57. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02148-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39979279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

