Pregnane X receptor activation alleviates renal fibrosis in mice via interacting with p53 and inhibiting the Wnt7a/β-catenin signaling
- PMID: 37344564
- PMCID: PMC10545797
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-023-01113-7
Pregnane X receptor activation alleviates renal fibrosis in mice via interacting with p53 and inhibiting the Wnt7a/β-catenin signaling
Abstract
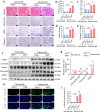
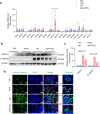
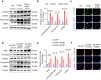
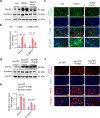
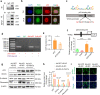
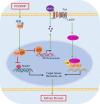
Renal fibrosis is a common pathological feature of chronic kidney disease (CKD) with various etiologies, which seriously affects the structure and function of the kidney. Pregnane X receptor (PXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and plays a critical role in regulating the genes related to xenobiotic and endobiotic metabolism in mammals. Previous studies show that PXR is expressed in the kidney and has protective effect against acute kidney injury (AKI). In this study, we investigated the role of PXR in CKD. Adenine diet-induced CKD (AD) model was established in wild-type and PXR humanized (hPXR) mice, respectively, which were treated with pregnenolone-16α-carbonitrile (PCN, 50 mg/kg, twice a week for 4 weeks) or rifampicin (RIF, 10 mg·kg-1·d-1, for 4 weeks). We showed that both PCN and RIF, which activated mouse and human PXR, respectively, improved renal function and attenuated renal fibrosis in the two types of AD mice. In addition, PCN treatment also alleviated renal fibrosis in unilateral ureter obstruction (UUO) mice. On the contrary, PXR gene deficiency exacerbated renal dysfunction and fibrosis in both adenine- and UUO-induced CKD mice. We found that PCN treatment suppressed the expression of the profibrotic Wnt7a and β-catenin in AD mice and in cultured mouse renal tubular epithelial cells treated with TGFβ1 in vitro. We demonstrated that PXR was colocalized and interacted with p53 in the nuclei of tubular epithelial cells. Overexpression of p53 increased the expression of Wnt7a, β-catenin and its downstream gene fibronectin. We further revealed that p53 bound to the promoter of Wnt7a gene to increase its transcription and β-catenin activation, leading to increased expression of the downstream profibrotic genes, which was inhibited by PXR. Taken together, PXR activation alleviates renal fibrosis in mice via interacting with p53 and inhibiting the Wnt7a/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: PXR; Wnt7a; chronic kidney disease; p53; renal fibrosis; β-catenin.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

