Mastectomy with Reconstruction Including Robotic Endoscopic Surgery (MARRES): a prospective cohort study of the Korea Robot-Endoscopy Minimal Access Breast Surgery Study Group (KoREa-BSG) and Korean Breast Cancer Study Group (KBCSG)
- PMID: 37344780
- PMCID: PMC10283322
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-10978-0
Mastectomy with Reconstruction Including Robotic Endoscopic Surgery (MARRES): a prospective cohort study of the Korea Robot-Endoscopy Minimal Access Breast Surgery Study Group (KoREa-BSG) and Korean Breast Cancer Study Group (KBCSG)
Abstract
Background: Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy (RNSM) has emerged as a new treatment option for breast cancer and risk-reducing mastectomy (RRM) for women who have a high risk of pathogenic variants. Even though several studies have reported that RNSM is a feasible procedure, some argue that it should only be performed by specialized surgeons, and data on oncologic outcomes and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) are limited. Recently, the United States Food and Drug Administration and several surgeons warned that robotic breast surgery should be performed only by specialized surgeons and recommended that the benefits, risks, and alternatives of all available treatment options be discussed with patients so they can make informed treatment decisions. The Korea Robot-Endoscopy Minimal Access Breast Surgery Study Group (KoREa-BSG) has been established to evaluate, standardize, and teach this state-of-the-art procedure. We have designed a multicenter prospective cohort study entitled Mastectomy with Reconstruction Including Robot Endoscopic Surgery (MARRES) to report surgical, PRO, and oncologic outcomes.
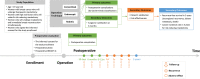
Methods: MARRES is a multi-institution cohort study prospectively collecting data from patients undergoing mastectomy and reconstruction. The patient inclusion criteria are adult women older than 19 with breast cancer or a high risk of breast cancer (patients with BRCA1/2, TP53, PALB2 mutations, etc.), who have scheduled therapeutic or RRM and want immediate reconstruction. Surgical outcomes, including pre- and postoperative photos, oncologic outcomes, cost-effectiveness, and PRO, are collected. The primary endpoints are postoperative complication rates within 30 postoperative days and the Clavien-Dindo grade of postoperative complications within 180 postoperative days. The secondary endpoints are 5-year postoperative recurrence-free survival and cancer incidence rate (for those who underwent RRM), patient satisfaction with reconstruction expectations preoperative (baseline) and results within 6 to 12 postoperative months, surgeon satisfaction with postoperative results in 6 postoperative months, and cost-effectiveness of the definitive surgery. Patient recruitment will be completed in April 2025, and the target number of enrolled patients is 2000.
Discussion: This study will provide evidence about the surgical outcomes, oncologic outcomes, and patient satisfaction with RNSM and endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM), compared with conventional NSM.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT04585074. Registered April 8, 2020.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; Conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy; Endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy; Germline BRCA1/2 mutation; Immediate breast reconstruction; Minimally invasive procedure; Robotic-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Hyung Seok Park received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Takeda, Ethicon, Medtronic, and Intuitive Surgical. Jai Min Ryu received a research grant from Medtronic for this study. No other relationships or activities have occurred that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Cocquyt VF, Blondeel PN, Depypere HT, Van De Sijpe KA, Daems KK, Monstrey SJ, Van Belle SJ. Better cosmetic results and comparable quality of life after skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate autologous breast reconstruction compared to breast conservative treatment. Br J Plast Surg. 2003;56(5):462–470. doi: 10.1016/S0007-1226(03)00198-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous