Human VDAC pseudogenes: an emerging role for VDAC1P8 pseudogene in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 37344914
- PMCID: PMC10286422
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-023-00446-1
Human VDAC pseudogenes: an emerging role for VDAC1P8 pseudogene in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Background: Voltage-dependent anion selective channels (VDACs) are the most abundant mitochondrial outer membrane proteins, encoded in mammals by three genes, VDAC1, 2 and 3, mostly ubiquitously expressed. As 'mitochondrial gatekeepers', VDACs control organelle and cell metabolism and are involved in many diseases. Despite the presence of numerous VDAC pseudogenes in the human genome, their significance and possible role in VDAC protein expression has not yet been considered.
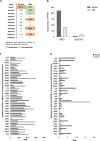
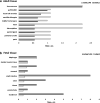
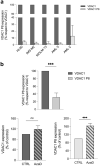
Results: We investigated the relevance of processed pseudogenes of human VDAC genes, both in physiological and in pathological contexts. Using high-throughput tools and querying many genomic and transcriptomic databases, we show that some VDAC pseudogenes are transcribed in specific tissues and pathological contexts. The obtained experimental data confirm an association of the VDAC1P8 pseudogene with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Conclusions: Our in-silico comparative analysis between the VDAC1 gene and its VDAC1P8 pseudogene, together with experimental data produced in AML cellular models, indicate a specific over-expression of the VDAC1P8 pseudogene in AML, correlated with a downregulation of the parental VDAC1 gene.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML); Competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs); Disease animal model; Pseudogene; Voltage-dependent anion selective channels (VDACs) gene.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Is the secret of VDAC Isoforms in their gene regulation? Characterization of human VDAC genes expression profile, promoter activity, and transcriptional regulators.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 7;21(19):7388. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197388. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33036380 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of syntenic relationships of VDAC1 pseudogenes for not only an understanding of the phylogenetic divergence history of rodents, but also ascertaining possible pseudogene candidates as genuine pseudogenes.Genomics. 2014 Aug;104(2):128-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2014.05.003. Epub 2014 May 22. Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24858958
-
VDAC isoforms in mammals.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1818(6):1466-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22020053 Review.
-
Protein-protein interaction networks as a new perspective to evaluate distinct functional roles of voltage-dependent anion channel isoforms.Mol Biosyst. 2017 Nov 21;13(12):2466-2476. doi: 10.1039/c7mb00434f. Mol Biosyst. 2017. PMID: 29028058 Review.
-
Arabidopsis Voltage-Dependent Anion Channels (VDACs): Overlapping and Specific Functions in Mitochondria.Cells. 2020 Apr 21;9(4):1023. doi: 10.3390/cells9041023. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326174 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in ALS.Genes (Basel). 2025 May 23;16(6):623. doi: 10.3390/genes16060623. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VDAC1-Targeted NHK1 Peptide Recovers Mitochondrial Dysfunction Counteracting Amyloid-β Oligomers Toxicity in Alzheimer's Disease.Aging Cell. 2025 Jul;24(7):e70069. doi: 10.1111/acel.70069. Epub 2025 Apr 13. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 40223243 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

