OSCC in Never-Smokers and Never-Drinkers Is Associated with Increased Expression of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Better Survival
- PMID: 37345025
- PMCID: PMC10216056
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15102688
OSCC in Never-Smokers and Never-Drinkers Is Associated with Increased Expression of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Better Survival
Abstract
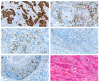
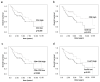
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical, histopathologic, and immunologic differences of oral squamous cell carcinoma of never-smokers/never-drinkers and smokers/drinkers. Immunohistochemical staining for CD4, CD8, FoxP3, CD1a, and p16 was performed in 131 oral squamous cell carcinomas from smokers/drinkers and never-smokers/never-drinkers. Associations of smoking/drinking status with clinicopathologic data, immunohistochemical antibody expression, and survival were examined. Oral squamous cell carcinoma in never-smokers/never-drinkers was associated with the female gender (p < 0.001). Never-smokers/never-drinkers were older at diagnosis than smokers/drinkers (p < 0.001). Never-smokers/never-drinkers had more tumors in the maxilla, mandible, and tongue (p < 0.001). Pre-existing oral potentially malignant disorders appeared to be more common in never-smokers/never-drinkers (p < 0.001). Perineural invasion was more common in smokers/drinkers (p = 0.039). Never-smoking/never-drinking was associated with better overall survival (p = 0.004) and disease-specific survival (p = 0.029). High CD4+ T cell infiltration was associated with never-smoking/never-drinking (p = 0.008). Never-smokers/never-drinkers also showed increased CD8+ T cell infiltration (p = 0.001) and increased FoxP3+ Treg infiltration (p = 0.023). Furthermore, the total group of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes was associated with never smoking/never drinking (p = 0.005). To conclude oral squamous cell carcinoma of the never-smokers/never-drinkers appears to be a distinct type of tumor, as it appears to have unique clinical and pathologic features and a more immunogenic microenvironment.
Keywords: CD1a; CD4; CD8; FoxP3; never-drinker; never-smoker; oral squamous cell carcinoma; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Blot W.J., McLaughlin J.K., Winn D.M., Austin D.F., Greenberg R.S., Preston-Martin S., Bernstein L., Schoenberg J.B., Stemhagen A., Fraumeni J.F. Smoking and drinking in relation to oral and pharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res. 1988;48:3282–3287. - PubMed
-
- Foy J.P., Bertolus C., Michallet M.C., Deneuve S., Incitti R., Bendriss-Vermare N., Albaret M.-A., Ortiz-Cuaran S., Thomas E., Colombe A. The immune microenvironment of HPV-Negative oral squamous cell carcinoma from Never-Smokers and Never-Drinkers patients suggests higher clinical benefit of IDO1 and PD1/PD-L1 blockade. Ann. Oncol. 2017;28:1934–1941. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx210. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

