Ostial vs. wide area circumferential ablation guided by the Ablation Index in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 37345859
- PMCID: PMC10286571
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euad160
Ostial vs. wide area circumferential ablation guided by the Ablation Index in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
Abstract
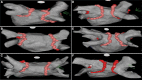
Aims: Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) guided by the Ablation Index (AI) has shown high acute and mid-term efficacy in the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF). Previous data before the AI-era had suggested that wide-area circumferential ablation (WACA) was preferable to ostial ablation. However, with the use of AI, we hypothesize that ostial circumferential ablation is non-inferior to WACA and can improve outcomes in paroxysmal AF.
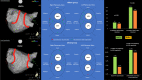
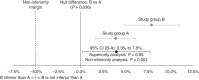
Methods and results: Prospective, multicentre, non-randomized, non-inferiority study of consecutive patients were referred for paroxysmal AF ablation from January 2020 to September 2021. All procedures were performed using the AI software, and patients were separated into two different groups: WACA vs. ostial circumferential ablation. Acute reconnection, procedural data, and 1-year arrhythmia recurrence were assessed. During the enrolment period, 162 patients (64% males, mean age of 60 ± 11 years) fulfilled the study inclusion criteria-81 patients [304 pulmonary vein (PV)] in the WACA group and 81 patients (301 PV) in the ostial group. Acute PV reconnection was identified in 7.9% [95% confidence interval (CI), 4.9-11.1%] of PVs in the WACA group compared with 3.3% (95% CI, 1.8-6.1%) of PVs in the ostial group [P < 0.001 for non-inferiority; adjusted odds ratio 0.51 (95% CI, 0.23-0.83), P = 0.05]. Patients in the WACA group had longer ablation (35 vs. 29 min, P = 0.001) and procedure (121 vs. 102 min, P < 0.001) times. No significant difference in arrhythmia recurrence was seen at 1-year of follow-up [11.1% in WACA vs. 9.9% in ostial, hazard ratio 1.13 (95% CI, 0.44-1.94), P = 0.80 for superiority].
Conclusion: In paroxysmal AF patients treated with tailored AI-guided PVI, ostial circumferential ablation is not inferior to WACA with regard to acute PV reconnection, while allowing quicker procedures with less ablation time.
Keywords: Ablation Index; Acute reconnection; Ostial circumferential; Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation; Pulmonary vein isolation; Wide-area circumferential ablation.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: P.A.S. has received consulting fees from Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Abbott. S.B. has received training grants from Biosense Webster and Biotronik. M.P. is an employee of Biosense Webster. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist Cet al. . 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the task force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
-
- Macle L, Khairy P, Weerasooriya R, Novak P, Verma A, Willems Set al. . Adenosine-guided pulmonary vein isolation for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: an international, multicentre, randomised superiority trial. Lancet 2015;386:672–9. - PubMed
-
- Taghji P, El Haddad M, Phlips T, Wolf M, Knecht S, Vandekerckhove Yet al. . Evaluation of a strategy aiming to enclose the pulmonary veins with contiguous and optimized radiofrequency lesions in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a pilot study. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 2018;4:99–108. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

