Regulation of T cell differentiation and function by long noncoding RNAs in homeostasis and cancer
- PMID: 37346034
- PMCID: PMC10281531
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181499
Regulation of T cell differentiation and function by long noncoding RNAs in homeostasis and cancer
Abstract
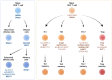
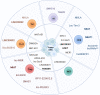
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) increase in genomes of complex organisms and represent the largest group of RNA genes transcribed in mammalian cells. Previously considered only transcriptional noise, lncRNAs comprise a heterogeneous class of transcripts that are emerging as critical regulators of T cell-mediated immunity. Here we summarize the lncRNA expression landscape of different T cell subsets and highlight recent advances in the role of lncRNAs in regulating T cell differentiation, function and exhaustion during homeostasis and cancer. We discuss the different molecular mechanisms of lncRNAs and highlight lncRNAs that can serve as novel targets to modulate T cell function or to improve the response to cancer immunotherapies by modulating the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: adoptive cell therapy; dysfunction; exhaustion; gamma delta T cell; noncoding RNA; regulatory T cell; tumor immune evasion; tumor-infiltrating T cell.
Copyright © 2023 Erber and Herndler-Brandstetter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

