Monitoring immunomodulation strategies in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 37346035
- PMCID: PMC10279879
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1206874
Monitoring immunomodulation strategies in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
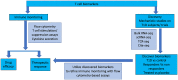
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a T-cell mediated autoimmune disease. Short-term treatment with agents targeting T cells, B cells and inflammatory cytokines to modify the disease course resulted in a short-term pause in disease activity. Lessons learnt from these trials will be discussed in this review. It is expected that effective disease-modifying agents will become available for use in earlier stages of T1D. Progress has been made to analyze antigen-specific T cells with standardization of T cell assay and discovery of antigen epitopes but there are many challenges. High-dimensional profiling of gene, protein and TCR expression at single cell level with innovative computational tools should lead to novel biomarker discovery. With this, assays to detect, quantify and characterize the phenotype and function of antigen-specific T cells will continuously evolve. An improved understanding of T cell responses will help researchers and clinicians to better predict disease onset, and progression, and the therapeutic efficacy of interventions to prevent or arrest T1D.
Keywords: T cell exhaustion; antigen specific therapy; biomarkers; disease modifying treatment; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2023 Krishnamurthy, Lacorcia, Kay, Thomas and Mannering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barbosa J, Chern MM, Anderson VE, Noreen H, Johnson S, Reinsmoen N, et al. . Linkage analysis between the major histocompatibility system and insulin-dependent diabetes in families with patients in two consecutive generations. J Clin Invest (1980) 65(3):592–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI109704 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

