The development of endoplasmic reticulum-related gene signatures and the immune infiltration analysis of sepsis
- PMID: 37346041
- PMCID: PMC10280294
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183769
The development of endoplasmic reticulum-related gene signatures and the immune infiltration analysis of sepsis
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is a complex condition involving multiorgan failure, resulting from the hosts' deleterious systemic immune response to infection. It is characterized by high mortality, with limited effective detection and treatment options. Dysregulated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is directly involved in the pathophysiology of immune-mediated diseases.
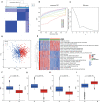
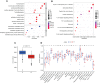
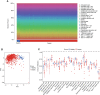
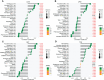
Methods: Clinical samples were obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus datasets (i.e., GSE65682, GSE54514, and GSE95233) to perform the differential analysis in this study. A weighted gene co-expression network analysis algorithm combining multiple machine learning algorithms was used to identify the diagnostic biomarkers for sepsis. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment, and the single-sample gene set enrichment analysis algorithm were used to analyze immune infiltration characteristics in sepsis. PCR analysis and western blotting were used to demonstrate the potential role of TXN in sepsis.
Results: Four ERRGs, namely SET, LPIN1, TXN, and CD74, have been identified as characteristic diagnostic biomarkers for sepsis. Immune infiltration has been repeatedly proved to play a vital role both in sepsis and ER. Subsequently, the immune infiltration characteristics result indicated that the development of sepsis is mediated by immune-related function, as four diagnostic biomarkers were strongly associated with the immune infiltration landscape of sepsis. The biological experiments in vitro and vivo demonstrate TXN is emerging as crucial player in maintaining ER homeostasis in sepsis.
Conclusion: Our research identified novel potential biomarkers for sepsis diagnosis, which point toward a potential strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of sepsis.
Keywords: diagnostic biomarkers; endoplasmic reticulum; immune infiltration; machine learning; sepsis.
Copyright © 2023 Zhou, Chen, Li, Fu, Chen, Zhang, Luo and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of immune-related endoplasmic reticulum stress genes in sepsis using bioinformatics and machine learning.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 20;13:995974. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.995974. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36203606 Free PMC article.
-
LPIN1 Is a Regulatory Factor Associated With Immune Response and Inflammation in Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 9;13:820164. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.820164. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35222395 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenic cell death biomarkers for sepsis diagnosis and mechanism via integrated bioinformatics.Sci Rep. 2025 May 27;15(1):18575. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03282-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40425742 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based endoplasmic reticulum-related diagnostic biomarker and immune microenvironment landscape for osteoarthritis.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Feb 28;16(5):4563-4578. doi: 10.18632/aging.205611. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38428406 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel four-gene diagnostic signature for patients with sepsis by integrating weighted gene co-expression network analysis and support vector machine algorithm.Hereditas. 2022 Feb 21;159(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s41065-021-00215-8. Hereditas. 2022. PMID: 35184762 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of oxidative stress-related genes for the diagnosis of sepsis-induced acute lung injury.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 22;20(7):e0327945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327945. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40694561 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of m6A RNA methylation and ferroptosis-related biomarkers in sepsis: transcriptome combined with single-cell RNA sequencing.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 7;16:1543517. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543517. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40124361 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the Regulatory Network of Programmed Cell Death Genes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Blood-Derived circRNA Transcriptome Information and Single-Cell Multi-omics Data.Biochem Genet. 2024 Dec 10. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10989-x. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 39656402
-
Novel Identification of CD74 as a Biomarker for Diagnosing and Prognosing Sepsis Patients.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Mar 15;18:3829-3842. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S509089. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40115322 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of machine learning and protein‑protein interaction network established one ATM‑DPP4‑TXN ferroptotic diagnostic model with experimental validation.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Sep;32(3):239. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13604. Epub 2025 Jul 4. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40613196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Svendsen M, Steindal SA, Hamilton Larsen M, Trygg Solberg M. Comparison of the systematic inflammatory response syndrome and the quick sequential organ failure assessment for prognostic accuracy in detecting sepsis in the emergency department: a systematic review. Int Emerg Nurs (2023) 66:101242. doi: 10.1016/j.ienj.2022.101242 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

