A novel framework of multiclass skin lesion recognition from dermoscopic images using deep learning and explainable AI
- PMID: 37346069
- PMCID: PMC10281646
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1151257
A novel framework of multiclass skin lesion recognition from dermoscopic images using deep learning and explainable AI
Abstract
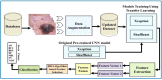
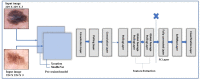
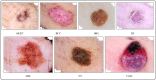
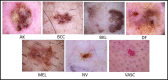
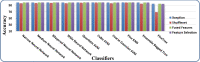
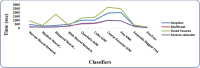
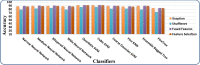
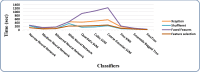
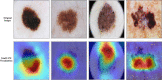
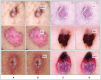
Skin cancer is a serious disease that affects people all over the world. Melanoma is an aggressive form of skin cancer, and early detection can significantly reduce human mortality. In the United States, approximately 97,610 new cases of melanoma will be diagnosed in 2023. However, challenges such as lesion irregularities, low-contrast lesions, intraclass color similarity, redundant features, and imbalanced datasets make improved recognition accuracy using computerized techniques extremely difficult. This work presented a new framework for skin lesion recognition using data augmentation, deep learning, and explainable artificial intelligence. In the proposed framework, data augmentation is performed at the initial step to increase the dataset size, and then two pretrained deep learning models are employed. Both models have been fine-tuned and trained using deep transfer learning. Both models (Xception and ShuffleNet) utilize the global average pooling layer for deep feature extraction. The analysis of this step shows that some important information is missing; therefore, we performed the fusion. After the fusion process, the computational time was increased; therefore, we developed an improved Butterfly Optimization Algorithm. Using this algorithm, only the best features are selected and classified using machine learning classifiers. In addition, a GradCAM-based visualization is performed to analyze the important region in the image. Two publicly available datasets-ISIC2018 and HAM10000-have been utilized and obtained improved accuracy of 99.3% and 91.5%, respectively. Comparing the proposed framework accuracy with state-of-the-art methods reveals improved and less computational time.
Keywords: deep features; dermoscopic images; explainable AI; feature selection; skin cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Ahmad, Shah, Khan, Baili, Ansari, Tariq, Kim and Cha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Saeed J, Zeebaree S. Skin lesion classification based on deep convolutional neural networks architectures. J Appl Sci Technol Trends (2021) 2:41–51. doi: 10.38094/jastt20189 - DOI
-
- Sultana NN, Puhan NB. (2018). Recent deep learning methods for melanoma detection: a review, in: International Conference on Mathematics and Computing. pp. 118–32.
-
- Anjum MA, Amin J, Sharif M, Khan HU, Malik MSA, Kadry S. Deep semantic segmentation and multi-class skin lesion classification based on convolutional neural network. IEEE Access (2020) 8:129668–78. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3009276 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

