Solar-driven seawater desalination via plasmonic hybrid MOF/polymer and its antibacterial activity
- PMID: 37346961
- PMCID: PMC10280044
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra02242k
Solar-driven seawater desalination via plasmonic hybrid MOF/polymer and its antibacterial activity
Abstract
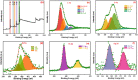
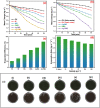
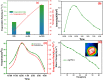
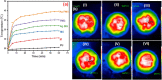
In recent years, solar seawater desalination has been considered to be a promising and cost-effective technique to produce clean sources for water treatment and water deficiency. In addition, this technique shows high photothermal conversion efficiency by solar collectors to transfer solar energy into heat and the transformation of molecules in the capillaries of solar evaporators. In this study, we report the preparation of graphene-supported MIL-125 with polyurethane foam (MGPU) for solar steam generation. We modified MGPU by using the plasmonic nanoparticles of Ag and a polymer of polyaniline to increase the evaporation rate. Polyurethane foam can float on the surface of water and self-pump water by its hydrophilic porous structure, superior thermal insulation capabilities, and easy fabrication. MIL-125 has a high salt rejection and higher water permeability. It can reduce the affinity between water molecules and the pore surface of membrane, making it simple for water molecules to move through the pores. GO is a great alternative for steam generation applications since it exhibits broad-band light. The strong solar absorption, photothermal conversion efficiency, and photoreaction efficiency are enhanced by the use of silver nanoparticles in the photoreaction. The salt resistance capability is enhanced in saline water in the presence of polyaniline in a composite. Under one solar irradiation, the Ag/PANI/GO@MIL-125 (Ag-PMG) nanocomposite demonstrates an average 1.26 kg m2 h-1 rate of evaporation and an efficiency as high as 90%. The composite exhibits remarkable stability and durability after more than 10 cycles of use without a noticeable decrease in activity. In addition, the composite exhibits excellent organic dye removal from contaminated water and generates pure condensed freshwater. The antibacterial photoactivity of the photocatalysts was examined against B. subtilis and E. coli. The results demonstrate that Ag-PMG shows higher antibacterial activity than MIL-125 and PMG. It was shown that the presence of rGO, PANI, and Ag in the sample enhances the antimicrobial activity.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
High efficiency solar desalination and dye retention of plasmonic/reduced graphene oxide based copper oxide nanocomposites.RSC Adv. 2021 Apr 22;11(25):15184-15194. doi: 10.1039/d1ra01663f. eCollection 2021 Apr 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35424040 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmonic chemically modified cotton nanocomposite fibers for efficient solar water desalination and wastewater treatment.Nanoscale. 2018 Oct 21;10(39):18531-18539. doi: 10.1039/c8nr05916k. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Nanoscale. 2018. PMID: 30221298
-
Compressible polyaniline-coated sodium alginate-cattail fiber foam for efficient and salt-resistant solar steam generation.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023 Sep;645:551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.04.182. Epub 2023 May 4. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023. PMID: 37163801
-
Reviewing wood-based solar-driven interfacial evaporators for desalination.Water Res. 2022 Sep 1;223:119011. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.119011. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Water Res. 2022. PMID: 36037711 Review.
-
Biomass-based materials for solar-powered seawater evaporation.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Feb 1;858(Pt 3):160003. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160003. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36370772 Review.
Cited by
-
Bandgap Engineering on UiO-66 Metal-Organic Framework Derivatives for Solar-Driven Seawater Desalination.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jul;12(26):e2502989. doi: 10.1002/advs.202502989. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40213834 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of Low-Cost Porous Carbon Polypropylene Composite Sheets with High Photothermal Conversion Performance for Solar Steam Generation.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Oct 4;16(19):2813. doi: 10.3390/polym16192813. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39408523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu Y. Ma J. Liu D. Xu H. Cui F. Wang W. Chem. Eng. J. 2019;356:869–876.
-
- Nayi K. H. Modi K. V. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2018;81:136–148.
-
- Ramalingam K. Liang M. Pyae N. L. W. Aung S. H. Oo T. Z. Srimuk P. Ma J. Presser V. Chen F. Waite T. D. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2020;12:32788–32796. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

