Dissecting the Arginine and Lysine Biosynthetic Pathways and Their Relationship in Haloarchaeon Natrinema gari J7-2 via Endogenous CRISPR-Cas System-Based Genome Editing
- PMID: 37347159
- PMCID: PMC10433800
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00288-23
Dissecting the Arginine and Lysine Biosynthetic Pathways and Their Relationship in Haloarchaeon Natrinema gari J7-2 via Endogenous CRISPR-Cas System-Based Genome Editing
Abstract
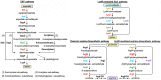
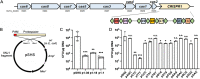
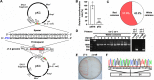
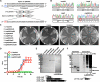
The evolutionary relationship between arginine and lysine biosynthetic pathways has been well established in bacteria and hyperthermophilic archaea but remains largely unknown in haloarchaea. Here, the endogenous CRISPR-Cas system was harnessed to edit arginine and lysine biosynthesis-related genes in the haloarchaeon Natrinema gari J7-2. The ΔargW, ΔargX, ΔargB, and ΔargD mutant strains display an arginine auxotrophic phenotype, while the ΔdapB mutant shows a lysine auxotrophic phenotype, suggesting that strain J7-2 utilizes the ArgW-mediated pathway and the diaminopimelate (DAP) pathway to synthesize arginine and lysine, respectively. Unlike the ArgD in Escherichia coli acting as a bifunctional aminotransferase in both the arginine biosynthesis pathway and the DAP pathway, the ArgD in strain J7-2 participates only in arginine biosynthesis. Meanwhile, in strain J7-2, the function of argB cannot be compensated for by its evolutionary counterpart ask in the DAP pathway. Moreover, strain J7-2 cannot utilize α-aminoadipate (AAA) to synthesize lysine via the ArgW-mediated pathway, in contrast to hyperthermophilic archaea that employ a bifunctional LysW-mediated pathway to synthesize arginine (or ornithine) and lysine from glutamate and AAA, respectively. Additionally, the replacement of a 5-amino-acid signature motif responsible for substrate specificity of strain J7-2 ArgX with that of its hyperthermophilic archaeal homologs cannot endow the ΔdapB mutant with the ability to biosynthesize lysine from AAA. The in vitro analysis shows that strain J7-2 ArgX acts on glutamate rather than AAA. These results suggest that the arginine and lysine biosynthetic pathways of strain J7-2 are highly specialized during evolution. IMPORTANCE Due to their roles in amino acid metabolism and close evolutionary relationship, arginine and lysine biosynthetic pathways represent interesting models for probing functional specialization of metabolic routes. The current knowledge with respect to arginine and lysine biosynthesis is limited for haloarchaea compared to that for bacteria and hyperthermophilic archaea. Our results demonstrate that the haloarchaeon Natrinema gari J7-2 employs the ArgW-mediated pathway and the DAP pathway for arginine and lysine biosynthesis, respectively, and the two pathways are functionally independent of each other; meanwhile, ArgX is a key determinant of substrate specificity of the ArgW-mediated pathway in strain J7-2. This study provides new clues about haloarchaeal amino acid metabolism and confirms the convenience and efficiency of endogenous CRISPR-Cas system-based genome editing in haloarchaea.
Keywords: CRISPR; arginine biosynthesis; diaminopimelate pathway; genome editing; haloarchaea; lysine biosynthesis; α-aminoadipate pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
HtrAs are essential for the survival of the haloarchaeon Natrinema gari J7-2 in response to heat, high salinity, and toxic substances.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Feb 21;90(2):e0204823. doi: 10.1128/aem.02048-23. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38289131 Free PMC article.
-
The complete genome sequence of Natrinema sp. J7-2, a haloarchaeon capable of growth on synthetic media without amino acid supplements.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041621. Epub 2012 Jul 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22911826 Free PMC article.
-
A TrmBL2-like transcription factor mediates the growth phase-dependent expression of halolysin SptA in a concentration-dependent manner in Natrinema gari J7-2.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Jul 24;90(7):e0074124. doi: 10.1128/aem.00741-24. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38953660 Free PMC article.
-
Surprising arginine biosynthesis: a reappraisal of the enzymology and evolution of the pathway in microorganisms.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 Mar;71(1):36-47. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00032-06. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17347518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next Generation Prokaryotic Engineering: The CRISPR-Cas Toolkit.Trends Biotechnol. 2016 Jul;34(7):575-587. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.02.004. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Trends Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26944793 Review.
Cited by
-
HtrAs are essential for the survival of the haloarchaeon Natrinema gari J7-2 in response to heat, high salinity, and toxic substances.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Feb 21;90(2):e0204823. doi: 10.1128/aem.02048-23. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38289131 Free PMC article.
-
A global perspective on the genomics of Moraxella catarrhalis.Microb Genom. 2025 Aug;11(8):001488. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001488. Microb Genom. 2025. PMID: 40844250 Free PMC article.
-
FBXW7 metabolic reprogramming inhibits the development of colon cancer by down-regulating the activity of arginine/mToR pathways.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 17;20(1):e0317294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317294. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39823500 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic engineering of Sorangium cellulosum reveals hidden enzymology in myxobacterial natural product biosynthesis.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 27;16(1):7996. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-63441-y. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40866386 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

