Tailored extraction and ion mobility-mass spectrometry enables isotopologue analysis of tetrahydrofolate vitamers
- PMID: 37347300
- PMCID: PMC10404201
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-023-04786-5
Tailored extraction and ion mobility-mass spectrometry enables isotopologue analysis of tetrahydrofolate vitamers
Abstract
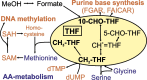
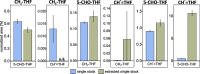
Climate change directs the focus in biotechnology increasingly on one-carbon metabolism for fixation of CO2 and CO2-derived chemicals (e.g. methanol, formate) to reduce our reliance on both fossil and food-competing carbon sources. The tetrahydrofolate pathway is involved in several one-carbon fixation pathways. To study such pathways, stable isotope-labelled tracer analysis performed with mass spectrometry is state of the art. However, no such method is currently available for tetrahydrofolate vitamers. In the present work, we established a fit-for-purpose extraction method for the methylotrophic yeast Komagataella phaffii that allows access to intracellular methyl- and methenyl-tetrahydrofolate (THF) with demonstrated stability over several hours. To determine isotopologue distributions of methyl-THF, LC-QTOFMS provides a selective fragment ion with suitable intensity of at least two isotopologues in all samples, but not for methenyl-THF. However, the addition of ion mobility separation provided a critical selectivity improvement allowing accurate isotopologue distribution analysis of methenyl-THF with LC-IM-TOFMS. Application of these new methods for 13C-tracer experiments revealed a decrease from 83 ± 4 to 64 ± 5% in the M + 0 carbon isotopologue fraction in methyl-THF after 1 h of labelling with formate, and to 54 ± 5% with methanol. The M + 0 carbon isotopologue fraction of methenyl-THF was reduced from 83 ± 2 to 78 ± 1% over the same time when using 13C-methanol labelling. The labelling results of multiple strains evidenced the involvement of the THF pathway in the oxygen-tolerant reductive glycine pathway, the presence of the in vivo reduction of formate to formaldehyde, and the activity of the spontaneous condensation reaction of formaldehyde with THF in K. phaffii.
Keywords: 13C-Labelling; Ion mobility-mass spectrometry; Isotopologue ratio analysis; Tetrahydrofolate pathway; Vitamers.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wei K, Guan H, Luo Q, He J, Sun S. Recent advances in CO2 capture and reduction. Nanoscale. 2022;14:11869–91. 10.1039/D2NR02894H - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

