Nonnegligible Seroprevalence and Predictors of Murine Typhus, Japan
- PMID: 37347821
- PMCID: PMC10310371
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2907.230037
Nonnegligible Seroprevalence and Predictors of Murine Typhus, Japan
Abstract
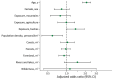
To elucidate the epidemiology of murine typhus, which is infrequently reported in Japan, we conducted a cross-sectional study involving 2,382 residents of rickettsiosis-endemic areas in Honshu Island during August-November 2020. Rickettsia typhi seroprevalence rate was higher than that of Orientia tsutsugamushi, indicating that murine typhus is a neglected disease.
Keywords: Japan; Japanese spotted fever; Orientia tsutsugamushi; Rickettsia japonica; Rickettsia typhi; bacteria; cross-sectional studies; flea borne; murine typhus; rickettsia; scrub typhus; seroepidemiological studies; spotted fever group rickettsiosis; typhus; vector-borne infections.
Figures

References
-
- Devamani CS, Schmidt WP, Ariyoshi K, Anitha A, Kalaimani S, Prakash JAJ. Risk factors for scrub typhus, murine typhus, and spotted fever seropositivity in urban areas, rural plains, and peri-forest hill villages in South India: a cross-sectional study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020;103:238–48. 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0642 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tamiya T. Recent advances in studies of tsutsugamushi disease in Japan. Tokyo: Medical Culture, Inc.; 1962. p. 53–54.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

