Genetic fine-mapping from summary data using a nonlocal prior improves the detection of multiple causal variants
- PMID: 37348543
- PMCID: PMC10326304
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad396
Genetic fine-mapping from summary data using a nonlocal prior improves the detection of multiple causal variants
Abstract
Motivation: Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been successful in identifying genomic loci associated with complex traits. Genetic fine-mapping aims to detect independent causal variants from the GWAS-identified loci, adjusting for linkage disequilibrium patterns.
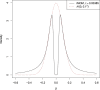
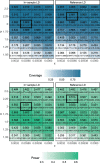
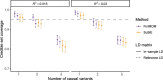
Results: We present "FiniMOM" (fine-mapping using a product inverse-moment prior), a novel Bayesian fine-mapping method for summarized genetic associations. For causal effects, the method uses a nonlocal inverse-moment prior, which is a natural prior distribution to model non-null effects in finite samples. A beta-binomial prior is set for the number of causal variants, with a parameterization that can be used to control for potential misspecifications in the linkage disequilibrium reference. The results of simulations studies aimed to mimic a typical GWAS on circulating protein levels show improved credible set coverage and power of the proposed method over current state-of-the-art fine-mapping method SuSiE, especially in the case of multiple causal variants within a locus.
Availability and implementation: https://vkarhune.github.io/finimom/.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SparsePro: An efficient fine-mapping method integrating summary statistics and functional annotations.PLoS Genet. 2023 Dec 28;19(12):e1011104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011104. eCollection 2023 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 38153934 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of expression QTLs with fine mapping via SuSiE.PLoS Genet. 2024 Jan 25;20(1):e1010929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010929. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38271473 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-Mapping the Results From Genome-Wide Association Studies of Primary Biliary Cholangitis Using SuSiE and h2-D2.Genet Epidemiol. 2025 Jan;49(1):e22592. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22592. Epub 2024 Oct 6. Genet Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 39370608 Free PMC article.
-
From genome-wide associations to candidate causal variants by statistical fine-mapping.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Aug;19(8):491-504. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0016-z. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29844615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine-mapping genetic associations.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Sep 30;29(R1):R81-R88. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa148. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32744321 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The goldmine of GWAS summary statistics: a systematic review of methods and tools.BioData Min. 2024 Sep 5;17(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13040-024-00385-x. BioData Min. 2024. PMID: 39238044 Free PMC article.
-
Towards improved fine-mapping of candidate causal variants.Nat Rev Genet. 2025 Jul 28. doi: 10.1038/s41576-025-00869-4. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Genet. 2025. PMID: 40721533 Review.
-
Improved genetic discovery and fine-mapping resolution through multivariate latent factor analysis of high-dimensional traits.Cell Genom. 2025 May 14;5(5):100847. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2025.100847. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Cell Genom. 2025. PMID: 40220762 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Human Genetics to Prioritize Coagulation Cascade Protein Targets for Ischemic Stroke Prevention.Stroke. 2025 Jun;56(6):1542-1553. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.124.049808. Epub 2025 Apr 6. Stroke. 2025. PMID: 40188416 Free PMC article.
-
Finemap-MiXeR: A variational Bayesian approach for genetic finemapping.PLoS Genet. 2024 Aug 15;20(8):e1011372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011372. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39146375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akdis M, Burgler S, Crameri R. et al. Interleukins, from 1 to 37, and interferon-gamma: receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;127:701–21.e1–70. - PubMed
-
- Barker A. Monte Carlo calculations of the radial distribution functions for a proton–electron plasma. Aust J Phys 1965;18:119.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

