New Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System: Inhibition of Brain Aminopeptidase A, ACE2 Ubiquitination, and Angiotensinogen
- PMID: 37348757
- PMCID: PMC10730775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cjca.2023.06.013
New Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System: Inhibition of Brain Aminopeptidase A, ACE2 Ubiquitination, and Angiotensinogen
Abstract
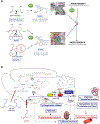
Despite the availability of various therapeutic classes of antihypertensive drugs, hypertension remains poorly controlled, in part because of poor adherence. Hence, there is a need for the development of antihypertensive drugs acting on new targets to improve control of blood pressure. This review discusses novel insights (including the data of recent clinical trials) with regard to interference with the renin-angiotensin system, focusing on the enzymes aminopeptidase A and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the brain, as well as the substrate of renin- angiotensinogen-in the liver. It raises the possibility that centrally acting amino peptidase A inhibitors (eg, firibastat), preventing the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin III in the brain, might be particularly useful in African Americans and patients with obesity. Firibastat additionally upregulates brain ACE2, allowing the conversion of angiotensin II to its protective metabolite angiotensin-(1-7). Furthermore, antisense oligonucleotides or small interfering ribonucleic acids suppress hepatic angiotensinogen for weeks to months after 1 injection and thus could potentially overcome adherence issues. Finally, interference with ACE2 ubiquitination is emerging as a future option for the treatment of neurogenic hypertension, given that ubiquitination resistance might upregulate ACE2 activity.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1923–1994. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e67–e492. - PubMed
-
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2020:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

