Bdellovibrio predation cycle characterized at nanometre-scale resolution with cryo-electron tomography
- PMID: 37349588
- PMCID: PMC11061892
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-023-01401-2
Bdellovibrio predation cycle characterized at nanometre-scale resolution with cryo-electron tomography
Abstract
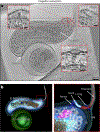
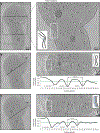
Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus is a microbial predator that offers promise as a living antibiotic for its ability to kill Gram-negative bacteria, including human pathogens. Even after six decades of study, fundamental details of its predation cycle remain mysterious. Here we used cryo-electron tomography to comprehensively image the lifecycle of B. bacteriovorus at nanometre-scale resolution. With high-resolution images of predation in a native (hydrated, unstained) state, we discover several surprising features of the process, including macromolecular complexes involved in prey attachment/invasion and a flexible portal structure lining a hole in the prey peptidoglycan that tightly seals the prey outer membrane around the predator during entry. Unexpectedly, we find that B. bacteriovorus does not shed its flagellum during invasion, but rather resorbs it into its periplasm for degradation. Finally, following growth and division in the bdelloplast, we observe a transient and extensive ribosomal lattice on the condensed B. bacteriovorus nucleoid.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Pérez J, Moraleda-Muñoz A, Marcos-Torres FJ & Muñoz-Dorado J Bacterial predation: 75 years and counting! Environ. Microbiol. 18, 766–779 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Stolp H & Starr MP Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus gen. et sp. n., a predatory, ectoparasitic, and bacteriolytic microorganism. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 29, 217–248 (1963). - PubMed
-
- Stolp H & Petzold H Untersuchungen über einen obligat parasitischen Mikroorganismus mit lytischer Aktivität für Pseudomonas-Bakterien. J. Phytopathol. 45, 364–390 (1962).
-
- Sockett RE Predatory lifestyle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 63, 523–539 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

