NFE2L3 drives hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by regulating the proteasome-dependent degradation of ISGylated p53
- PMID: 37350063
- PMCID: PMC10475773
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15887
NFE2L3 drives hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by regulating the proteasome-dependent degradation of ISGylated p53
Abstract
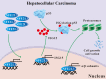
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 3 (NFE2L3) is a member of the cap 'n' collar basic-region leucine zipper (CNC-bZIP) transcription factor family that plays a vital role in modulating oxidation-reduction steady-state and proteolysis. Accumulating evidence suggests that NFE2L3 participates in cancer development; however, little is known about the mechanism by which NFE2L3 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell growth. Here, we confirmed that NFE2L3 promotes HCC cell proliferation by acting as a transcription factor, which directly induces the expression of proteasome and interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) to enhance the proteasome-dependent degradation of ISGylated p53. Post-translational ISGylation abated the stability of p53 and facilitated HCC cell growth. In summary, we uncovered the pivotal role of NFE2L3 in promoting HCC cell proliferation during proteostasis. This finding may provide a new target for the clinical treatment of HCC.
Keywords: ISGylation; NFE2L3; cell proliferation; p53; proteasome.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 3 exhibits tumor-suppressing effects in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Mar 14;25(10):1210-1223. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i10.1210. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30886504 Free PMC article.
-
NRF3-POMP-20S Proteasome Assembly Axis Promotes Cancer Development via Ubiquitin-Independent Proteolysis of p53 and Retinoblastoma Protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Apr 28;40(10):e00597-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00597-19. Print 2020 Apr 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32123008 Free PMC article.
-
NFE2L1 and NFE2L3 Complementarily Maintain Basal Proteasome Activity in Cancer Cells through CPEB3-Mediated Translational Repression.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jun 29;40(14):e00010-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00010-20. Print 2020 Jun 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32366381 Free PMC article.
-
NFE2L3 (NRF3): the Cinderella of the Cap'n'Collar transcription factors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Oct;68(20):3337-48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0747-x. Epub 2011 Jun 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21687990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New addiction to the NRF2-related factor NRF3 in cancer cells: Ubiquitin-independent proteolysis through the 20S proteasome.Cancer Sci. 2020 Jan;111(1):6-14. doi: 10.1111/cas.14244. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31742837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New insight into the CNC-bZIP member, NFE2L3, in human diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 23;12:1430486. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1430486. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39149514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic regulation of immune checkpoint molecules by redox regulators CNC-bZIP transcription factors.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 20;15(1):685. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01574-0. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39565431 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Multifaceted Roles of ISG15: From Immunomodulation to Therapeutic Frontiers.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;12(2):153. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12020153. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38400136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway.Open Life Sci. 2023 Nov 23;18(1):20220790. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0790. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 38027228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7‐33. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Zhang Y, Guo X. Proteasome dysregulation in human cancer: implications for clinical therapies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017;36:703‐716. - PubMed
-
- Gęgotek A, Skrzydlewska E. Białka CNC w fizjologii i patologii [CNC proteins in physiology and pathology]. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015;69:729‐743. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 22SXQT0221/Cooperation Project of Nanchong Science and Technology
- 20SXCXTD0004/Cooperation Project of Nanchong Science and Technology
- 82172928/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022NSFSC0731/Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
- CBY19-YZ16/Research Development Fund of North Sichuan Medical College
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

