Comprehensive essentiality analysis of the Mycobacterium kansasii genome by saturation transposon mutagenesis and deep sequencing
- PMID: 37350613
- PMCID: PMC10470612
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.00573-23
Comprehensive essentiality analysis of the Mycobacterium kansasii genome by saturation transposon mutagenesis and deep sequencing
Abstract
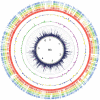
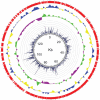
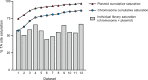
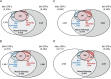
Mycobacterium kansasii (Mk) is an opportunistic pathogen that is frequently isolated from urban water systems, posing a health risk to susceptible individuals. Despite its ability to cause tuberculosis-like pulmonary disease, very few studies have probed the genetics of this opportunistic pathogen. Here, we report a comprehensive essentiality analysis of the Mk genome. Deep sequencing of a high-density library of Mk Himar1 transposon mutants revealed that 86.8% of the chromosomal thymine-adenine (TA) dinucleotide target sites were permissive to insertion, leaving 13.2% TA sites unoccupied. Our analysis identified 394 of the 5,350 annotated open reading frames (ORFs) as essential. The majority of these essential ORFs (84.8%) share essential mutual orthologs with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). A comparative genomics analysis identified 139 Mk essential ORFs that share essential orthologs in four other species of mycobacteria. Thirteen Mk essential ORFs share orthologs in all four species that were identified as being not essential, while only two Mk essential ORFs are absent in all species compared. We used the essentiality data and a comparative genomics analysis reported here to highlight differences in essentiality between candidate Mtb drug targets and the corresponding Mk orthologs. Our findings suggest that the Mk genome encodes redundant or additional pathways that may confound validation of potential Mtb drugs and drug target candidates against the opportunistic pathogen. Additionally, we identified 57 intergenic regions containing four or more consecutive unoccupied TA sites. A disproportionally large number of these regions were located upstream of pe/ppe genes. Finally, we present an essentiality and orthology analysis of the Mk pRAW-like plasmid, pMK1248. IMPORTANCE Mk is one of the most common nontuberculous mycobacterial pathogens associated with tuberculosis-like pulmonary disease. Drug resistance emergence is a threat to the control of Mk infections, which already requires long-term, multidrug courses. A comprehensive understanding of Mk biology is critical to facilitate the development of new and more efficacious therapeutics against Mk. We combined transposon-based mutagenesis with analysis of insertion site identification data to uncover genes and other genomic regions required for Mk growth. We also compared the gene essentiality data set of Mk to those available for several other mycobacteria. This analysis highlighted key similarities and differences in the biology of Mk compared to these other species. Altogether, the genome-wide essentiality information generated and the results of the cross-species comparative genomics analysis represent valuable resources to assist the process of identifying and prioritizing potential Mk drug target candidates and to guide future studies on Mk biology.
Keywords: Mycobacterium kansasii; TnSeq; antitubercular target candidate; comparative mycobacterial gene essentiality; gene essentiality; mycobacterial ESX secretion system; mycobacterial comparative genomics; mycobacterial drug targets; mycobacterial orthology analysis; nontuberculous mycobacteria; nucleoid-associated protein; pRAW-like plasmid; plasmid-encoded ESX system; transposon mutagenesis; tuberculosis; type VII secretion system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Essentiality Analysis of Mycobacterium abscessus by Saturated Transposon Mutagenesis and Deep Sequencing.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0104921. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01049-21. Epub 2021 Jun 15. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34126767 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Essentiality Analysis of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Genome via Saturating Transposon Mutagenesis.mBio. 2017 Jan 17;8(1):e02133-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02133-16. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28096490 Free PMC article.
-
Transposon mutagenesis in Mycobacterium kansasii links a small RNA gene to colony morphology and biofilm formation and identifies 9,885 intragenic insertions that do not compromise colony outgrowth.Microbiologyopen. 2020 Apr;9(4):e988. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.988. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Microbiologyopen. 2020. PMID: 32083796 Free PMC article.
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
-
Mycobacterial Pathogenomics and Evolution.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Feb;2(1):MGM2-0025-2013. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MGM2-0025-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26082120 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Underpinnings of Carotenogenesis and Light-Induced Transcriptome Remodeling in the Opportunistic Pathogen Mycobacterium kansasii.Pathogens. 2023 Jan 5;12(1):86. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12010086. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36678434 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of essential mycobacterial gene glmM reduces pathogen survival and induces host-protective immune responses against tuberculosis.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 6;7(1):949. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06620-9. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39107377 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

