Delayed presentation of biopsy-proven eosinophilic myocarditis following COVID-19 mRNA vaccine
- PMID: 37351099
- PMCID: PMC10282781
- DOI: 10.21542/gcsp.2023.10
Delayed presentation of biopsy-proven eosinophilic myocarditis following COVID-19 mRNA vaccine
Abstract
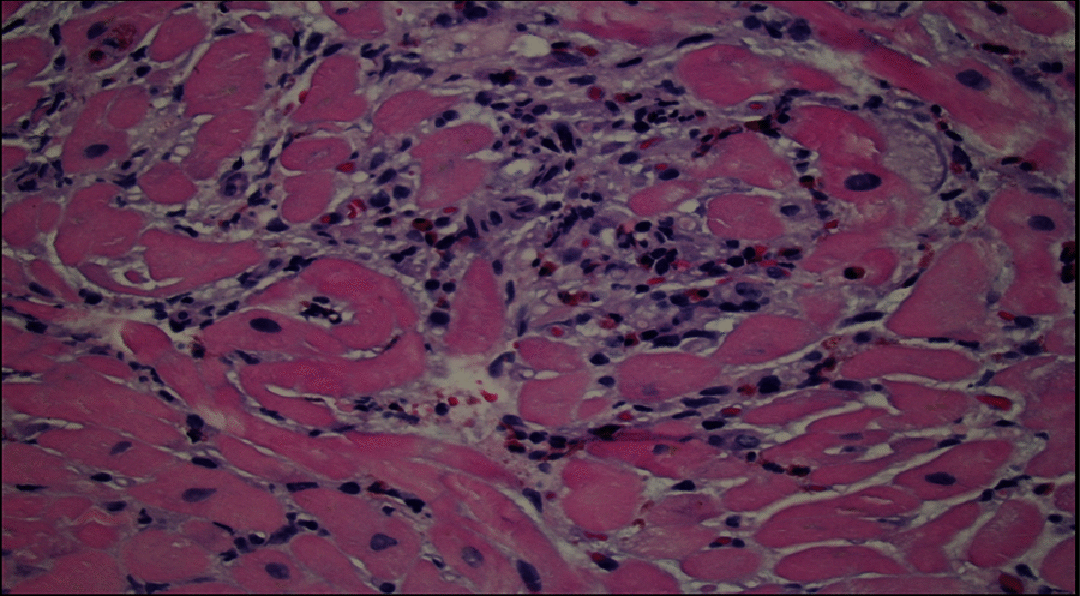
Myopericarditis associated with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines has been recognized as an uncommon adverse reaction, especially among young, healthy adult males. Eosinophilic myocarditis is a rare form of inflammation reflecting a hypersensitivity reaction following an inciting event commonly caused by drugs including vaccines. Eosinophilic myocarditis, a subtype of myocarditis, is characterized by eosinophilic myocardial infiltrates. It is usually accompanied by systemic eosinophilia in the form of a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome and is rarely associated with myocyte fibrosis and/or necrosis. In this report, we present a case of biopsy-proven eosinophilic myocarditis in a 24-year-old male patient, likely secondary to COVID-19 mRNA vaccination. To our knowledge, this is the first report to describe delayed eosinophilic myocarditis following the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. Clinicians should be aware of possible delayed presentation to avoid associated morbidity.
Copyright ©2023 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Istampoulouoglou I, Dimitriou G, Späni S, Christ A, Zimmermanns B, Koechlin S, Stoeckmann O, Winterhalder C, Marono D, Toma V, Leuppi-Taegtmeyer AB. Myocarditis and pericarditis in association with COVID-19 mRNA-vaccination: cases from a regional pharmacovigilance centre. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2021;2021(3):e202118. doi: 10.21542/gcsp.2021.18. doi: PMID: 34805376; PMCID: PMC8587334. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marshall M, Ferguson ID, Lewis P, Jaggi P, Gagliardo C, Collins JS, Shaughnessy R, Caron R, Fuss C, Corbin KJE, Emuren L, Faherty E, Hall EK, Di Pentima C, Oster ME, Paintsil E, Siddiqui S, Timchak DM, Guzman-Cottrill JA. Symptomatic acute myocarditis in 7 adolescents after Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. Pediatrics. 2021;148(3):e2021052478. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052478. doi: Epub 2021 Jun 4. PMID: 34088762. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosner CM, Genovese L, Tehrani BN, Atkins M, Bakhshi H, Chaudhri S, Damluji AA, de Lemos JA, Desai SS, Emaminia A, Flanagan MC, Khera A, Maghsoudi A, Mekonnen G, Muthukumar A, Saeed IM, Sherwood MW, Sinha SS, O’Connor CM, deFilippi CR. Myocarditis temporally associated with COVID-19 vaccination. Circulation. 2021;144(6):502–505. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055891. doi: Epub 2021 Jun 16. PMID: 34133885; PMCID: PMC8340723. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources