Multimodal laparoscopic coincidence gamma imaging system for near-infrared fluorescence guided surgery: a preclinical study
- PMID: 37351312
- PMCID: PMC10284170
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.10.3.033505
Multimodal laparoscopic coincidence gamma imaging system for near-infrared fluorescence guided surgery: a preclinical study
Abstract
Purpose: Minimally invasive surgery has advantages in terms of quality of life and patient outcomes. Recently, near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence guided surgery has widely used for preclinical and clinical trials. However, NIR fluorescence has a maximum penetration capability of 10 mm. Radiographic imaging can be a solution to overcome the depth issue of NIR fluorescence. For this reason, the performance of the multimodal imaging system, which integrates annihilation gamma (511 keV) rays, NIR fluorescence, and color images, was evaluated.
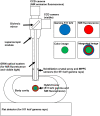
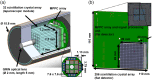
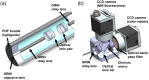
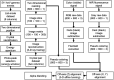
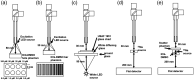
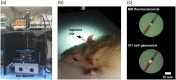
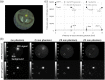
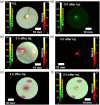
Approach: The multimodal imaging system consisted of a laparoscopic module, containing an internal detector for annihilation gamma events and cameras for optical imaging, and a flat module for coincidence detection with the internal detector. The acquired images were integrated by an algorithm with post image processing and registration. To evaluate the performance of the proposed multimodal imaging system, the images of a resolution target, a square bar target filled with a fluorescence dye, and a sodium-22 point source were analyzed. A preclinical test for axillary sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy with a rat model was conducted.
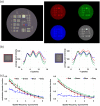
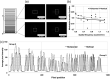
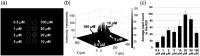
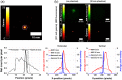
Results: The spatial resolution of color images was equivalent to 4 lp/mm. The modulation transfer function of NIR fluorescence at 1 lp/mm was 0.83. The 511 keV gamma sensitivity and spatial resolution of the point source were 0.54 cps/kBq and 2.1 mm, respectively. The image of 511 keV gamma rays showed almost the same intensity regardless of the thickness of the tissue phantom. In the preclinical test, an integrated image of the SLN sample of the rat model was obtained with the proposed multimodal imaging system.
Conclusions: With the proposed laparoscopic system, a merged image of the sample was obtained with the rat model. The annihilation gamma rays showed penetration capability with the tissue-mimicking phantom superior to that of NIR fluorescence.
Keywords: annihilation gamma ray; fluorescence guided surgery; image reconstruction; minimally invasive surgery; multimodal imaging system; near-infrared fluorescence.
© 2023 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization and validation of multimodal annihilation-gamma/near-infrared/visible laparoscopic system.J Biomed Opt. 2019 Sep;24(9):1-11. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.9.096008. J Biomed Opt. 2019. PMID: 31564072 Free PMC article.
-
A feasibility study of an integrated NIR/gamma/visible imaging system for endoscopic sentinel lymph node mapping.Med Phys. 2017 Jan;44(1):227-239. doi: 10.1002/mp.12029. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28102947
-
Intraoperative combined color and fluorescent images-based sentinel node mapping in the porcine lung: comparison of indocyanine green with or without albumin premixing.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013 Dec;146(6):1509-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.02.044. Epub 2013 Mar 21. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013. PMID: 23522603
-
Diagnostic value of near-infrared or fluorescent indocyanine green guided sentinel lymph node mapping in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Surg Oncol. 2018 Dec;118(8):1243-1256. doi: 10.1002/jso.25285. Epub 2018 Oct 31. J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30380146
-
Recent advances in near-infrared fluorescence-guided imaging surgery using indocyanine green.Surg Today. 2015 Dec;45(12):1467-74. doi: 10.1007/s00595-015-1158-7. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Surg Today. 2015. PMID: 25820596 Review.
Cited by
-
Initial demonstration of the Scratch-PET concept: an intraoperative PET with a hand-held detector.Radiol Phys Technol. 2025 Jun;18(2):407-416. doi: 10.1007/s12194-025-00889-z. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Radiol Phys Technol. 2025. PMID: 40072801 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

