Metallohelices stabilize DNA three-way junctions and induce DNA damage in cancer cells
- PMID: 37351627
- PMCID: PMC10415117
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad536
Metallohelices stabilize DNA three-way junctions and induce DNA damage in cancer cells
Abstract
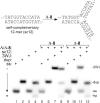
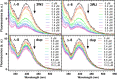
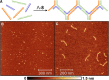
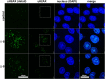
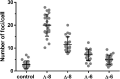
DNA three-way junctions (3WJ) represent one of the simplest supramolecular DNA structures arising as intermediates in homologous recombination in the absence of replication. They are also formed transiently during DNA replication. Here we examine the ability of Fe(II)-based metallohelices to act as DNA 3WJ binders and induce DNA damage in cells. We investigated the interaction of eight pairs of enantiomerically pure Fe(II) metallohelices with four different DNA junctions using biophysical and molecular biology methods. The results show that the metallohelices stabilize all types of tested DNA junctions, with the highest selectivity for the Y-shaped 3WJ and minimal selectivity for the 4WJ. The potential of the best stabilizer of DNA junctions and, at the same time, the most selective 3WJ binder investigated in this work to induce DNA damage was determined in human colon cancer HCT116 cells. These metallohelices proved to be efficient in killing cancer cells and triggering DNA damage that could yield therapeutic benefits.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cationic FeII Triplex-Forming Metallohelices as DNA Bulge Binders.Chemistry. 2020 Dec 9;26(69):16554-16562. doi: 10.1002/chem.202004060. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Chemistry. 2020. PMID: 33026666
-
FeII Metallohelices Stabilize DNA G-Quadruplexes and Downregulate the Expression of G-Quadruplex-Regulated Oncogenes.Chemistry. 2021 Aug 11;27(45):11682-11692. doi: 10.1002/chem.202101388. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Chemistry. 2021. PMID: 34048082
-
Optically Pure Metallohelices That Accumulate in Cell Nuclei, Condense/Aggregate DNA, and Inhibit Activities of DNA Processing Enzymes.Inorg Chem. 2020 Mar 2;59(5):3304-3311. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c00092. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Inorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32064865
-
Lighting up metallohelices: from DNA binders to chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy.Chem Commun (Camb). 2020 Jul 14;56(55):7537-7548. doi: 10.1039/d0cc02194f. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Chem Commun (Camb). 2020. PMID: 32573609 Review.
-
Non-covalent Metallo-Drugs: Using Shape to Target DNA and RNA Junctions and Other Nucleic Acid Structures.Met Ions Life Sci. 2018 Feb 5;18:/books/9783110470734/9783110470734-017/9783110470734-017.xml. doi: 10.1515/9783110470734-017. Met Ions Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29394030 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane lipid composition directs the cellular selectivity of antimicrobial metallohelices.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Mar 5;16(5):2249-2260. doi: 10.1039/d4md00973h. eCollection 2025 May 22. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40110349 Free PMC article.
-
Supramolecular Recognition of a DNA Four-Way Junction by an M2L4 Metallo-Cage, Inspired by a Simulation-Guided Design Approach.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Jun 24;64(26):e202504866. doi: 10.1002/anie.202504866. Epub 2025 May 5. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40243103 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive cancer targeting by programmable aptamer-tethered nanostructures.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 20;5(11):e775. doi: 10.1002/mco2.775. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39434968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Switching on Supramolecular DNA Junction Binding Using a Human Enzyme.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 May;64(21):e202503683. doi: 10.1002/anie.202503683. Epub 2025 Mar 23. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40088149 Free PMC article.
-
Ni(II) Cylinders Damage DNA in Cancer Cells and Preferentially Bind Y-Shaped DNA Three-Way Junctions Blocking DNA Synthesis.Small. 2024 Dec;20(52):e2406814. doi: 10.1002/smll.202406814. Epub 2024 Oct 20. Small. 2024. PMID: 39428899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leonard C.J., Berns K.I.. Adeno-associated virus type 2: a latent life cycle. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1994; 48:29–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

