Micro-paper-based analytical device decorated with metal-organic frameworks for the assay of synthetic cannabinoids in oral fluids coupled to ion mobility spectrometry
- PMID: 37351649
- PMCID: PMC10289984
- DOI: 10.1007/s00604-023-05844-6
Micro-paper-based analytical device decorated with metal-organic frameworks for the assay of synthetic cannabinoids in oral fluids coupled to ion mobility spectrometry
Abstract
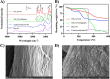
A new concept of paper-based device has been developed combining the advantages of cellulose supports and the rich surface chemistry of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). The composite, named as NH2-UiO-66@paper, has been developed for the isolation of synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists (SCRAs) in oral fluids, trying to mimic the interactions of those compounds with the human CB1R and CB2R receptors, mainly governed by hydrogen bonding and π-interactions with serine and histidine residues. MOF selection (UiO-66) and functionalization of the ligand (2-aminoterephthalic acid) has been done according to the following criteria: (i) water stability of the selected MOF, and (ii) promoting appropriate interactions with SCRAs due to the MOF nature. NH2-UiO-66@paper composite has been characterized in depth and the results confirmed that the material is stable at the temperature selected for thermal desorption (230 °C). Furthermore, the developed method provided appropriate precision values (RSD < 12%) and a limit of detection as low as 10 ng using ion mobility spectrometry as analytical technique. Lastly, the method has been successfully applied to the isolation of several synthetic cannabinoids from oral fluids. This method claims to be an interesting approach for expanding the combination of MOFs with sustainable support and represents a promising alternative to sophisticated and non-portable systems due to the negligible sample treatment required and the simplicity of the operation, which can be applied with screening purposes.
Keywords: Biological samples; Drugs; Paper-based devices; Solid-phase extraction; UiO-66.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metal-organic frameworks as promising solid-phase sorbents for the isolation of third-generation synthetic cannabinoids in biological samples.Anal Chim Acta. 2023 Mar 15;1246:340887. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2023.340887. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Anal Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 36764780
-
[Utilization of UiO-66-NH2@cellulose hybrid aerogel for solid-phase extraction of sildenafil in health products].Se Pu. 2022 Jun;40(6):556-564. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.11022. Se Pu. 2022. PMID: 35616201 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Determination of four phenolic endocrine-disrupting chemicals in water by dispersive solid-phase extraction-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on metal-organic skeleton porous carbon materials].Se Pu. 2024 Mar 8;42(3):264-274. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.05012. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 38503703 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A comprehensive review on water remediation using UiO-66 MOFs and their derivatives.Chemosphere. 2022 Sep;302:134845. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134845. Epub 2022 May 4. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35525446 Review.
-
[Research progress in application of metal-organic framework-derived materials to sample pretreatment].Se Pu. 2021 Sep;39(9):941-949. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.05017. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34486833 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Hussain CM (2020) Handbook on miniaturization in analytical chemistry: application of nanotechnology. Elsevier
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous