Physiological response of anthocyanin synthesis to different light intensities in blueberry
- PMID: 37352171
- PMCID: PMC10289459
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283284
Physiological response of anthocyanin synthesis to different light intensities in blueberry
Abstract
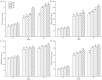
Fruit color is an important economic character of blueberry, determined by the amount of anthocyanin content. Anthocyanin synthesis within the blueberry fruits is significantly affected by light. To reveal the physiological response mechanism of anthocyanin synthesis in blueberry fruits in different light intensities, four light intensities (100% (CK), 75%, 50% and 25%) were set for the 'O'Neal' southern highbush blueberry as the experimental material in our study. The relationship between endogenous hormones content, associated enzyme activities, and variations with the anthocyanin content in blueberry fruits under various light intensities during the white fruit stage (S1), purple fruit stage (S2), and blue fruit stage (S3) were studied. The results showed that adequate light could significantly promote anthocyanin synthesis in blueberry fruits (P < 0.05). Blueberry fruits had an anthocyanin content that was 1.76~24.13 times higher under 100% light intensity than it was under non-full light intensity. Different light intensities significantly affected the content of endogenous hormones and the activity of associated enzymes in anthocyanin synthesis pathway (P < 0.05). Among them, the JA (jasmonic acid) content and PAL (phenylalanine ammonia lyase) activity of fruits under 100% light intensity were 2.49%~41.83% and 2.47%~48.48% higher than those under other light intensity, respectively. And a significant correlation was found between the variations in anthocyanin content in fruits and the content or activities of JA, ABA (abscisic acid), ETH (ethylene), GA3 (gibberellin 3), IAA (indoleacetic acid), PAL, CHI (chalcone isomerase), DFR (dihydroflavonol reductase) and UFGT (UDP-glucose: flavonoid 3-glucosyltransferase) (P < 0.05). It indicated that 100% light intensity significantly promoted anthocyanin synthesis in blueberry fruits by affecting endogenous hormones content and associated enzyme activities in the anthocyanin synthesis pathway. This study will lay a foundation for further research on the molecular mechanism of light intensity regulating anthocyanin synthesis in blueberry.
Copyright: © 2023 An et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Cheng YD, Liu LQ, Yuan C, Guan JF. Molecular Characterization of Ethylene-Regulated Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plums During Fruit Ripening. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2016; 34(4): 777–785. doi: 10.1007/s11105-015-0963-x - DOI
-
- Li XH, Uddin MR, Park WT, Kim YB, Seo JM, Kim SJ, et al.. Accumulation of anthocyanin and related genes expression during the development of cabbage seedlings. Process Biochemistry, 2014; 49(7):1084–1091. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2014.03.008 - DOI
-
- Sheoran IS, Dumonceaux T, Datla R, Sawhney VK. Anthocyanin accumulation in the hypocotyl of an ABA, ver producing male: terile tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) mutant Physiologia Plantarum, 2006; 127(4): 681–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00697.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

