Chemical profile and analysis of biosynthetic pathways and genes of volatile terpenes in Pityopsis ruthii, a rare and endangered flowering plant
- PMID: 37352235
- PMCID: PMC10289357
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287524
Chemical profile and analysis of biosynthetic pathways and genes of volatile terpenes in Pityopsis ruthii, a rare and endangered flowering plant
Erratum in
-
Correction: Chemical profile and analysis of biosynthetic pathways and genes of volatile terpenes in Pityopsis ruthii, a rare and endangered flowering plant.PLoS One. 2025 Sep 19;20(9):e0333001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0333001. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40971356 Free PMC article.
Abstract
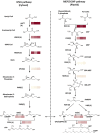
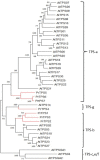
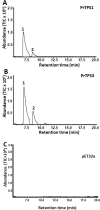
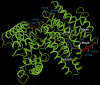
It is critical to gather biological information about rare and endangered plants to incorporate into conservation efforts. The secondary metabolism of Pityopsis ruthii, an endangered flowering plant that only occurs along limited sections of two rivers (Ocoee and Hiwassee) in Tennessee, USA was studied. Our long-term goal is to understand the mechanisms behind P. ruthii's adaptation to restricted areas in Tennessee. Here, we profiled the secondary metabolites, specifically in flowers, with a focus on terpenes, aiming to uncover the genomic and molecular basis of terpene biosynthesis in P. ruthii flowers using transcriptomic and biochemical approaches. By comparative profiling of the nonpolar portion of metabolites from various tissues, P. ruthii flowers were rich in terpenes, which included 4 monoterpenes and 10 sesquiterpenes. These terpenes were emitted from flowers as volatiles with monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes accounting for almost 68% and 32% of total emission of terpenes, respectively. These findings suggested that floral terpenes play important roles for the biology and adaptation of P. ruthii to its limited range. To investigate the biosynthesis of floral terpenes, transcriptome data for flowers were produced and analyzed. Genes involved in the terpene biosynthetic pathway were identified and their relative expressions determined. Using this approach, 67 putative terpene synthase (TPS) contigs were detected. TPSs in general are critical for terpene biosynthesis. Seven full-length TPS genes encoding putative monoterpene and sesquiterpene synthases were cloned and functionally characterized. Three catalyzed the biosynthesis of sesquiterpenes and four catalyzed the biosynthesis of monoterpenes. In conclusion, P. ruthii plants employ multiple TPS genes for the biosynthesis of a mixture of floral monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, which probably play roles in chemical defense and attracting insect pollinators alike.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Congress U. Endangered species act. US Code. 1973;16:1534–44.
-
- New York and Oxford: efloras.org; 2006 [cited 2023 2023-03-06].
-
- Moore PA, Wadl PA, Skinner JA, Trigiano RN, Bernard EC. Current knowledge, threats, and future efforts to sustain populations of Pityopsis ruthii (Asteraceae), an endangered southern Appalachian species. The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society. 2016;143(2):117–34.
-
- White AJ. An autecological study of the endangered species, Heterotheca ruthii (Small) Harms: University of Tennessee, Knoxville; 1977.
-
- Ruth’s Golden Aster (Pityopsis ruthii). 5-year review: Summary and evaluation: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service; 2018. [cited 2023 2023-03-06]. Available from: https://ecos.fws.gov/docs/five_year_review/doc5953.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

